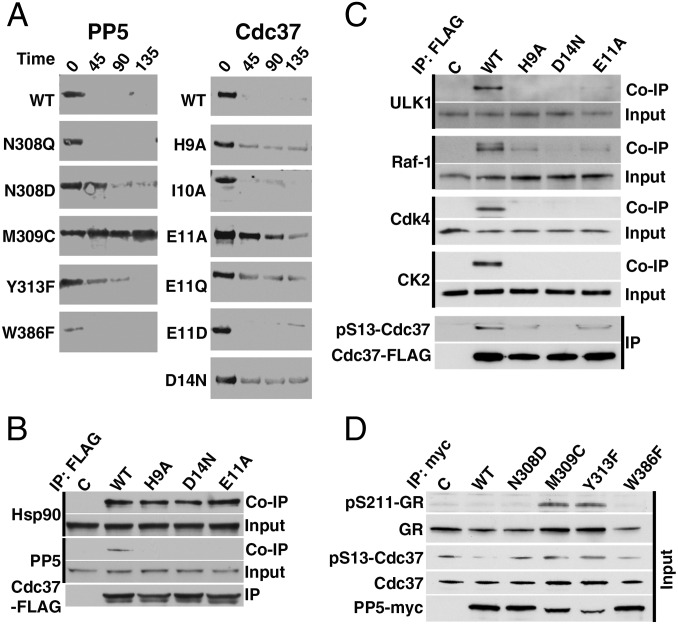
Fig. 3.
Structure-based mutations reveal the functional importance of specific interactions between PP5 and substrate in vitro and in vivo. (A) Dephosphorylation of phospho–Cdc37-Ser13 in the context of purified, full-length WT and indicated mutants of Cdc37 and PP5 in the presence of Hsp90. Activity was assessed using a phosphospecific antibody over time (minutes). (B) HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with empty plasmid (C), WT Cdc37-FLAG, or indicated mutants. Cdc37-FLAG proteins were subject to immunoprecipitation (IP). Co-IP of Hsp90 and PP5 was examined by immunoblotting. (C) HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with C, WT Cdc37-FLAG, or indicated mutants. Cdc37-FLAG proteins were subject to IP, and the level of phospho-Ser13 was examined by immunoblotting. Co-IP of CK2 and Hsp90 client kinases CDK4, Raf-1, and ULK1 was also examined by immunoblotting. (D) Total protein lysates were prepared from HEK293 cells transiently transfected with empty plasmid (C), WT PP5–c-myc, or indicated mutants. Cdc37, phospho–Ser13-Cdc37, GR, and phospho GR-211 protein levels were examined by immunoblotting.