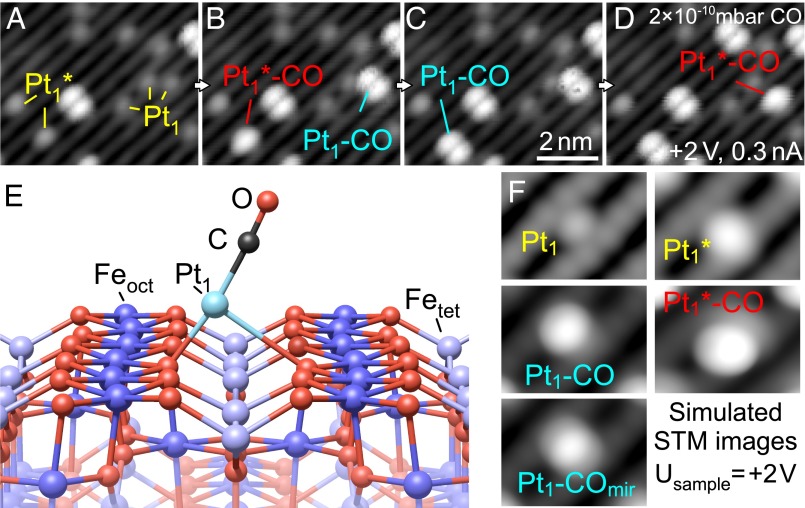
Fig. 2.
CO adsorption and Pt site interchange. (A–D) STM image sequence (same place) acquired during exposure to 2 × 10−10 mbar CO. (A) Pt adatoms in two configurations (Pt1, Pt1*) and bright, double-lobed features are observed. (B) CO adsorption on Pt1 and Pt1 * adatoms results in bright, double-lobed and oval features, respectively. (C) The Pt1*–CO labeled in red in B changes site, transforming into a Pt1–CO feature. (D) The Pt1–CO formed and labeled in cyan in B transforms into a Pt1 *–CO feature. (E) Structural model of Pt1–CO/Fe3O4(001). Upon adsorption of CO, the Pt adatom is lifted up and shifts perpendicular to the Fe rows to an off-centered position. (F) Simulated STM images at +2-V sample bias: Pt adatom, Pt* adatom, Pt1–CO, mirrored Pt1–CO. The latter is an overlay image of Pt1–CO in the two equivalent off-centered positions to simulate switching during the scan, induced thermally or by the STM tip.