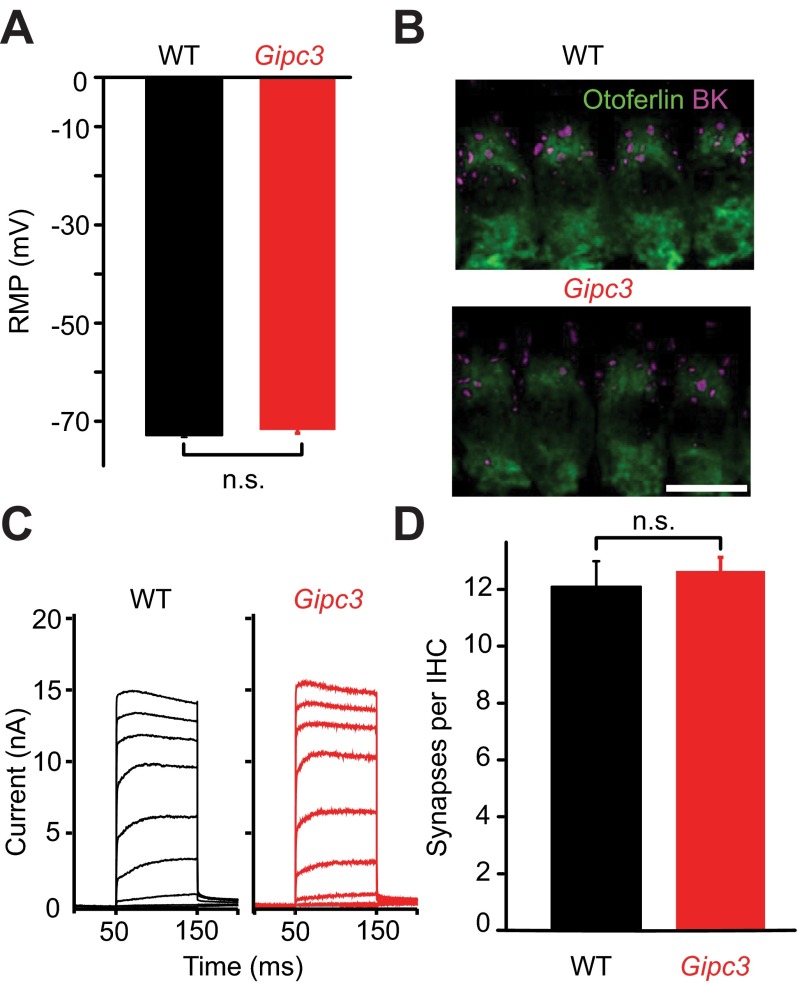
Fig. S7.
Increased whole-cell Ca2+ current but largely maintained IHC K+ currents and synapses in IHCs of Gipc3 mutant mice. (A) The resting membrane potential as recorded in the current-clamp configuration was normal in Gipc3 mutant IHCs: 71.7 ± 0.7 mV, n = 12 for Gipc3 mutant IHCs vs. −72.8 ± 0.5 mV; n = 19, for WT IHCs (P = 0.21, both p14–16). (B) Maximum projection of confocal section of immunolabeled organs of Corti: Gipc3 mutant IHCs (visualized by otoferlin immunofluorescence) show clusters of large-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels (magenta) at their “neck” region. (C) Representative potassium currents in Gipc3 mutant and WT IHCs: no obvious reduction due to Gipc3 disruption. (D) Normal number of ribbon synapses in Gipc3 mutant IHCs of 2-wk-old mice (12.09 ± 0.9, n = 28 for WT, 12.6 ± 0.5, n = 44 for Gipc3, P = 0.48). Analysis was performed on confocal stacks of organs of Corti following immunolabeling for RIBEYE/CtBP2 and postsynaptic GluA2/3.