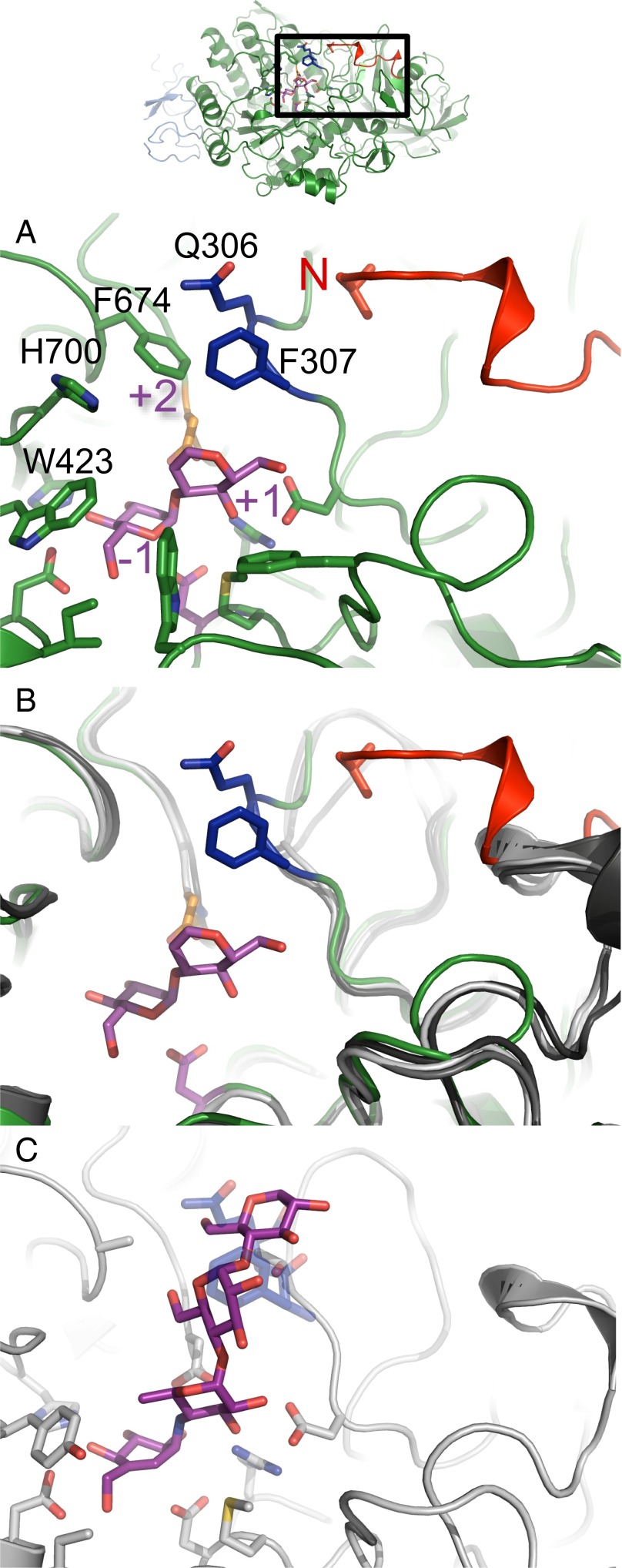
Fig. 3.
α-Subunit N terminus extension and exclusion loop insertion are previously unidentified α-GluII-specific determinants of enzyme activity. (A) Mmα-GluIITryps α-subunit (green) with its bound disaccharide substrate analog (purple). The enzyme’s subsites −1, +1, and +2 are indicated in purple lettering. The position of the α-subunit N terminus is highlighted in red, next to the exclusion loop insertion F307 and Q308 (dark blue). The exclusion loop insertion F307, Q308 is only present in α-GluII. The N-terminal V33 residue is shown in stick representation. (B) Structural alignment of Mmα-GluIITryps α-subunit (green) with its bound disaccharide substrate analog (purple) against the structures of H. sapiens intestinal α-glucosidases: N-terminal MGAM (light gray, PDB ID code 2QMJ), C-terminal MGAM (dark gray, PDB ID code 3TOP), and N-terminal SI (black, PDB ID code 3LPP). (C) Details of acarbose [purple (C atoms) and red (O atoms)] binding to human MGAM in PDB entry (gray, ID code 2QMJ). This mode of binding of acarbose is not possible in α-GluII due to steric hindrance from the exclusion loop residues F307 and Q308 (transparent dark blue).