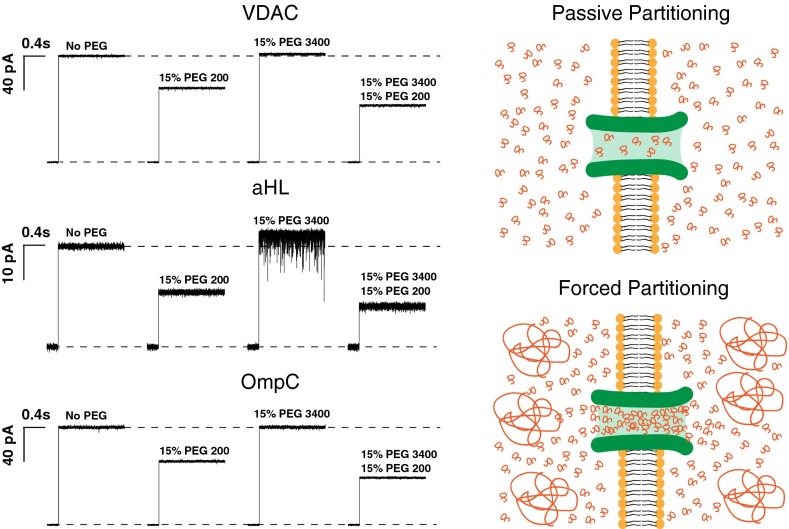
Fig. 3.
The effect of differently sized PEGs and their mixtures on channel conductance. Traces labeled “No PEG” show the current jump right after spontaneous channel formation. Addition of 15% (wt/wt) PEG200 causes a significant drop in single channel conductance (VDAC, 30%; aHL, 45%; and OmpC, 35%). Addition of 15% (wt/wt) PEG 3400, which does not penetrate the channel at this concentration, causes an apparent increase in single-channel conductance (VDAC, 2%; aHL, 10%; and OmpC, 2%). Addition of 15% (wt/wt) PEG200 along with 15% (wt/wt) of PEG3400 drops the channel conductance by an extra 15%, due to additional PEG200 partitioning into the pore, as it is“pushed” by PEG3400 molecules in the bathing solution. Current jumps after PEG addition correspond to the moments of transmembrane voltage application of 30 mV.