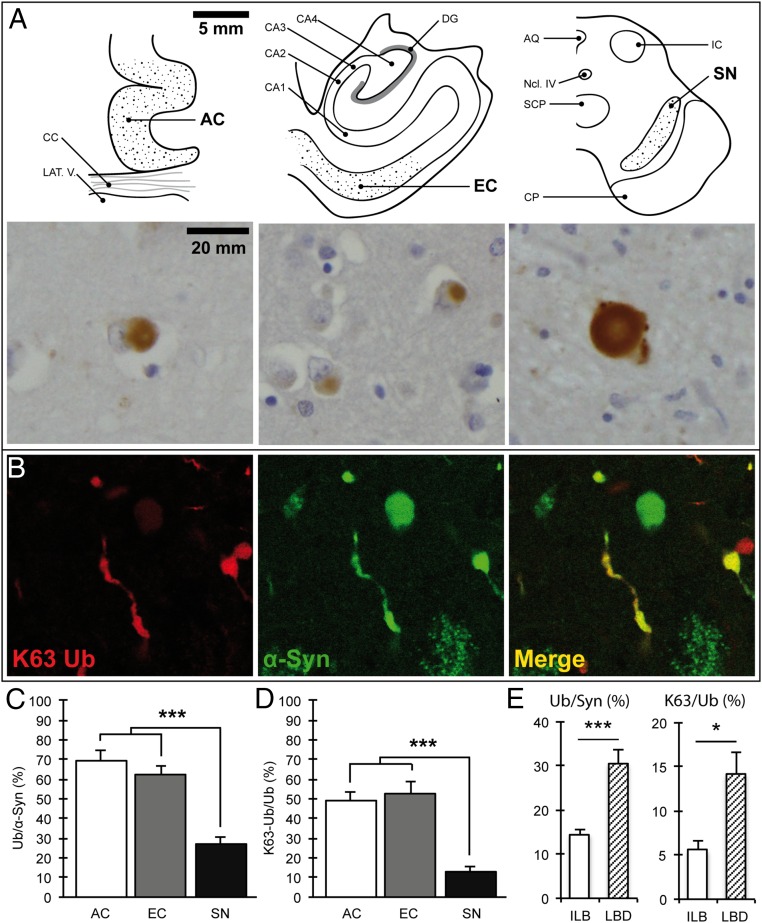
Fig. 1.
K63-linked ubiquitin conjugates are detected in α-synuclein–positive inclusions and are reduced in the substantia nigra. (A) Schematic view of the studied brain regions and corresponding light microscopy images showing K63-linked ubiquitinated inclusions. [Scale bars, 5 mm (schemes) and 20 mm (images).] (B) Confocal immunofluorescence showing colocalization of K63-linked ubiquitin chains and α-synuclein in Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites in nigral neurons. (C) Quantification of ubiquitin-positive inclusions as a percentage of α-synuclein–positive inclusions (Ub/α-Syn) in serial sections of the AC, EC, and SN; ***P < 0.0001, n = 14. (D) Quantification of K63-linked ubiquitinated inclusions as a percentage of ubiquitin–positive inclusions (K63-Ub/Ub) in serial sections of the AC, EC, and SN; ***P < 0.0001, n = 14. (E) The percentage of ubiquitinated inclusions in nigral neurons was low irrespective of the stage of disease and lower in incidental Lewy body compared with Lewy body disease cases. Ub/Syn, ***P < 0.0001, n = 14; K63/Syn, *P < 0.05, n = 14. AQ, central aqueduct; CA1–4, cornu ammonis 1–4; CC, corpus callosum; CP, corticopontine and pyramidal tracts; DG, dentate gyrus; IC, inferior colliculus; LAT.V., lateral ventricle; Ncl IV, trochlear nucleus; SCP, superior cerebellar peduncle. Error bars correspond to standard error of the mean.