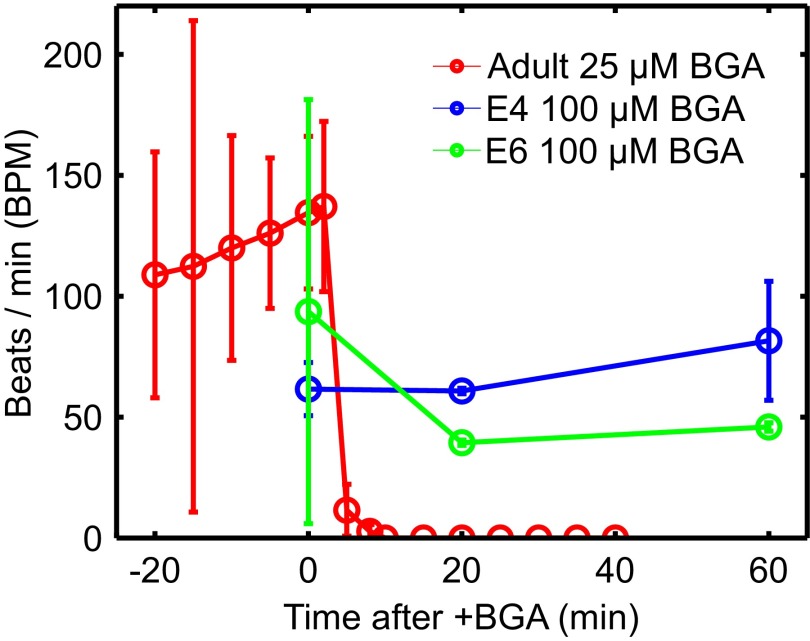
Fig. 4.
Conduction interference results for isolated hearts from three murine adults and four chicken embryos. Gap junctions are disrupted by perfusing intact adult (red) and embryonic E4 and E6 (blue and green, respectively) hearts with β-glycyrrhetinic acid (BGA). Heart functionality is quantified by beats per minute (BPM). Adult hearts stop beating after 10 min at 25 μM BGA (Movie S2). Embryonic hearts perfused at higher 100 μM show little to no effect after an hour. See Fig. S3 for adult heart BPM controls and Fig. S4 for control experiments on embryonic heart BGA perfusion.