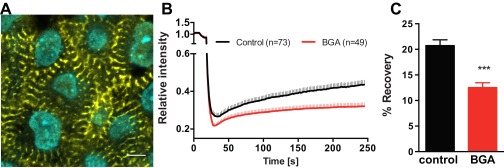
Fig. S4.
A displays a representative image of E4 chicken embryonic CMs stained for α-actinin and DNA. Image was taken 4 μm below the surface in the outflow tract of the looping heart. (Scale bar: 5 μm.) As exampled here, CMs in the E4 heart exhibit premature periodic striations, suggesting myofibrillogenesis of CMs. These cells were subjected to testing for effective gap junction interference via FRAP. B shows aggregated results from calcein red-orange FRAP experiments in control and BGA-treated E4 avian hearts. Individual CMs within the tissue were selected and photobleached (see example, Movie S3). Fluorescent intensity recovery was tracked over at 4 min in 49 +BGA CMs and 73 −BGA CMs. Rapid early recovery is likely due to intracellular diffusion and is unaffected by BGA treatment. In contrast, BGA treatment disrupts prolonged recovery, which is likely mediated by intercellular transport through gap junctions. C demonstrates the significantly higher fluorescence recovery after 4 min in control hearts, demonstrating BGA efficacy in disrupting E4 avian heart gap junctions. ***P < 0.001, unpaired Student's t test.