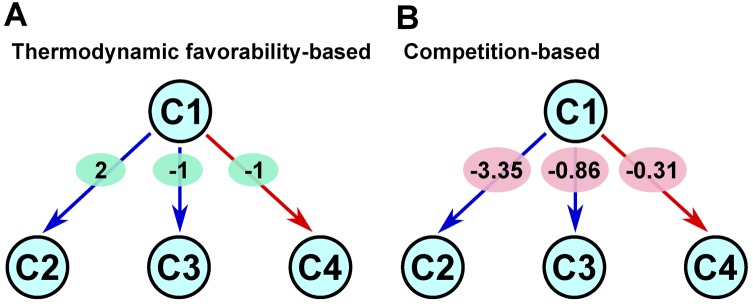
Figure 3.
An illustration of differences between the thermodynamic favorability-based weighting scheme and our competition-based weighting scheme. Nodes are metabolites and edges are metabolic conversions via reactions. Red edges indicate native reactions, while blue edges indicate foreign reactions. (A) The thermodynamic favorability based approach. The value within a green oval for each edge represents the weight ΔrG′°/RT where R is the gas constant and T is the absolute temperature. (B) The competition-based approach. For each edge, the value within a pink oval represents its weight. With this scheme, edges with the same ΔrG′° value can have different weights in a host-dependent fashion. For example, the weight of C1 → C3 is ln [e1/(1 + e1 + e1)], while that of C1 → C4 is ln [e1/(1 + e1)].