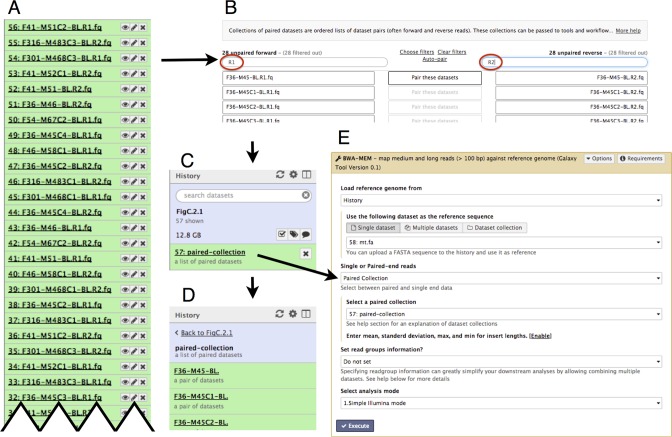
Figure 4.
(A) Dataset collections simplify analysis of large numbers of files. A Galaxy history with a paired-end DNA re-sequencing dataset from 28 individuals contains 56 files (each green box is a file). It is difficult to understand this history because there are so many files and because forward (R1) and reverse (R2) reads are unordered. As these files are analyzed and more outputs/files are created, it becomes very difficult to navigate around the history and understand how files are connected as inputs and outputs of particular tools or analyses. Dataset collections make analysis of this mix of files straightforward by grouping all files into a collection that can be analyzed as a single unit. This example demonstrates using collections with paired end data, but collections can be created for any set of files. (B) Creation of a paired collection from the history shown in panel A. Because dataset names use a uniform nomenclature for forward and reverse reads, the collection creation form can automatically determine pairings. (C) Pairing these datasets generates a single item (a Collection) in Galaxy's history. (D) Clicking on this newly created Collection expands it and shows its content (only first three datasets are shown). (E) Galaxy's BWA interface takes the entire dataset collection as a single input.