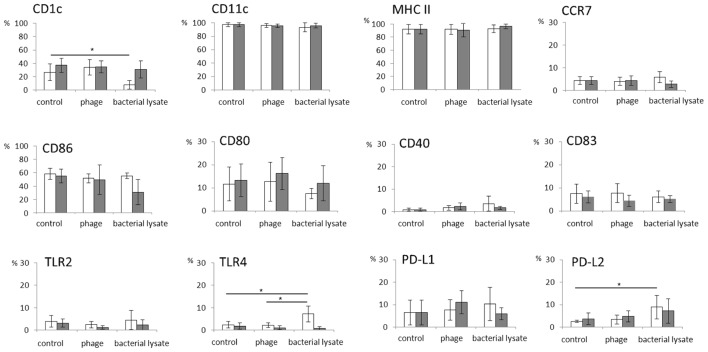
FIGURE 1.
The effects of bacteriophages and bacteriophage-generated bacterial lysates on the expression of markers associated with the differentiation of myeloid dendritic cells and their role in T cell activation. Human myeloid dendritic cells (mDCs) were differentiated from monocytes during five-day cultures with IL-4 (100 ng/ml) and GM-CSF (250 ng/ml) in the presence of individual phage preparations including purified preparation of T4 (white bars,  ), T4-generated Escherichia coli lysate (white bars,
), T4-generated Escherichia coli lysate (white bars,  ), purified preparation of A3/R (gray bars,
), purified preparation of A3/R (gray bars,  ), or A3/R-generated Staphylococcus aureus lysate (gray bars,
), or A3/R-generated Staphylococcus aureus lysate (gray bars,  ). In control cultures cells were treated with equal volumes of PBS. The expression of all markers including CD40, CD80, CD83, CD86, CD1c, CD11c, MHC class II, PD-L1, PD-L2, TLR2, TLR4, and CCR7 was determined by flow cytometry. The bars show the percentages of mDCs expressing individual markers. The experiment was repeated five times. *p < 0.05.
). In control cultures cells were treated with equal volumes of PBS. The expression of all markers including CD40, CD80, CD83, CD86, CD1c, CD11c, MHC class II, PD-L1, PD-L2, TLR2, TLR4, and CCR7 was determined by flow cytometry. The bars show the percentages of mDCs expressing individual markers. The experiment was repeated five times. *p < 0.05.