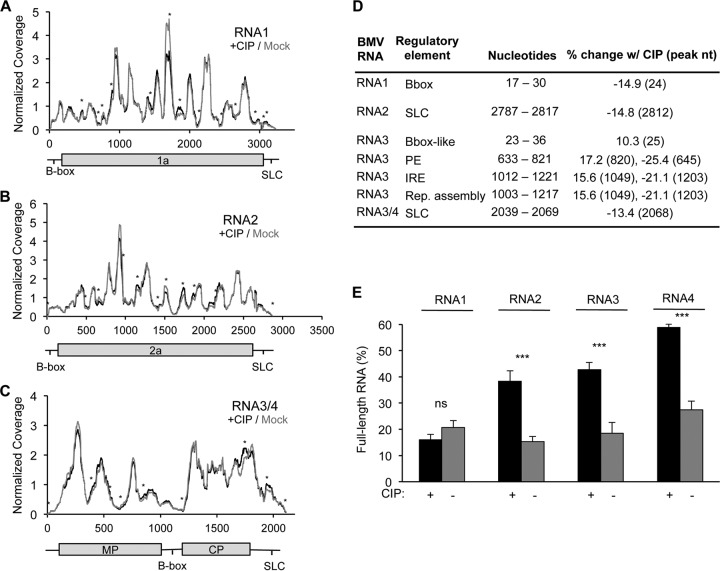
FIG 6.
Phosphorylation of the BMV capsid affects the capsid-RNA interaction. (A to C) The number of RNA sequences contacting the capsid within mock-treated and CIP-treated virions identified by CLIP-seq analysis. Normalized coverage is shown. The identities of the majority of sequences that contact the capsid do not change as a function of capsid phosphorylation, but differences in intensity were observed. Peaks with an asterisk represent those with a greater than 20% change following CIP treatment. MP, movement protein; SLC, stem loop C. (D) Previously characterized BMV RNA regulatory elements that had at least a 10% change in expression following CIP treatment. The nucleotides column displays the locations of the regulatory elements. The final column shows the percent change following CIP treatment, and the nucleotide position where the change was observed is given in parentheses. PE, packaging element; IRE, intergenic replication enhancer; Rep., replication. (E) Resistance to RNase A digestion, as measured by the abundance of intact RNA derived from B1 and B2.3/4 virions before and after CIP treatment, followed by RNase treatment. Black, CIP-treated samples; gray, mock-treated samples. The range for 1 standard deviation is shown. ns, no significant difference; ***, P < 0.005.