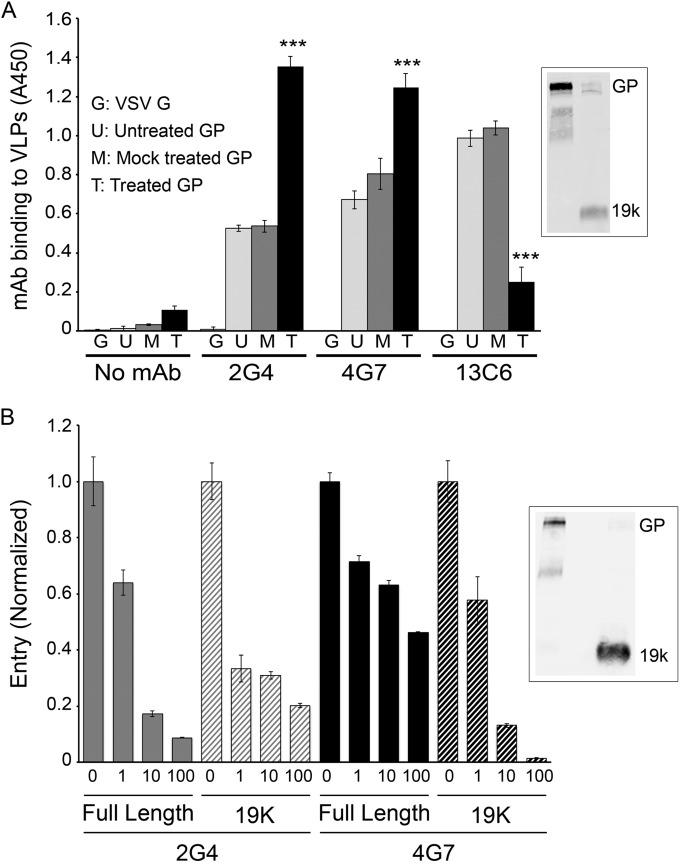
FIG 5.
MAbs c2G4 and c4G7 bind to 19-kDa EBOV GP on VLPs and block VLP entry mediated by 19-kDa GP. (A) VLPs bearing EBOV-Makona GP were untreated, mock treated, or (thermolysin) treated and then bound (triplicate samples) to high-bind ELISA plates as described in Materials and Methods. VLPs bearing VSV-G were used as a control. After blocking and washing (see Materials and Methods), 50 μg/ml MAb c2G4, c4G7, or c13C6 (PBS for control) were added, and the plate was processed and analyzed to detect MAb binding as described in Materials and Methods. Error bars represent the SD. ***, P < 0.001 ([thermolysin]-treated GP versus mock-treated GP). For the inset, cleavage of full-length GP to 19 kDa was confirmed by Western blotting with the anti-GP1 F88 rabbit antibody as described in Materials and Methods. Lane 1, mock-treated GP; lane 2, (thermolysin)-treated GP. The band labeled GP runs at 130 kDa, indicating that it is full-length GP with its mucin-like domain intact. (b) VLPs bearing Mayinga GP were untreated or (thermolysin) treated as described in Materials and Methods. After quenching the thermolysin, the VLPs were incubated with 50 μg/ml c2G4, c4G7, or PBS (Mock), as indicated, for 1 h at 37°C. Entry was then assayed, as described in the legend to Fig. 2. The entry level of untreated VLPs with full-length GP was 60%, and that of VLPs with (thermolysin)-treated (19 kDa) GP was 35%. Error bars represent the SD. Highly similar results were seen in two additional experiments (full-length mock-treated entry levels, 45 and 40%; 19-kDa mock-treated entry levels, 20 and 25%). Cleavage of full-length GP (130 kDa) to 19 kDa was confirmed by Western blotting with MAb H3C8 as described in Materials and Methods. Lane 1, untreated; lane 2, blank; lane 3, (thermolysin) treated.