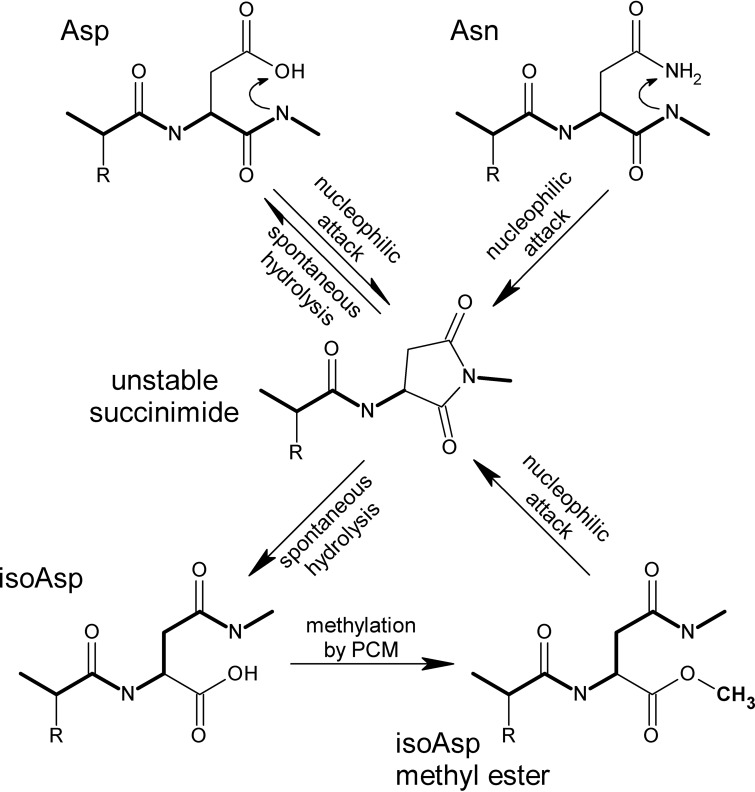
FIG 1.
Formation and repair of isoaspartyl residues in proteins. Isoaspartyl (isoAsp) damage results from spontaneous nucleophilic attack (top) of the peptide-bond nitrogen on the side chain carbonyl group of an aspartyl (Asp) or asparaginyl (Asn) residue, resulting in an unstable succinimide intermediate (middle), which hydrolyzes spontaneously to form isoAsp or reform Asp. The formation of isoAsp “kinks” the peptide backbone (heavy line) and alters the charge (in the case of Asn) or spatial relationships. Methylation of isoAsp by PCM (bottom) stimulates reformation of the intermediate, allowing for net repair to normal Asp.