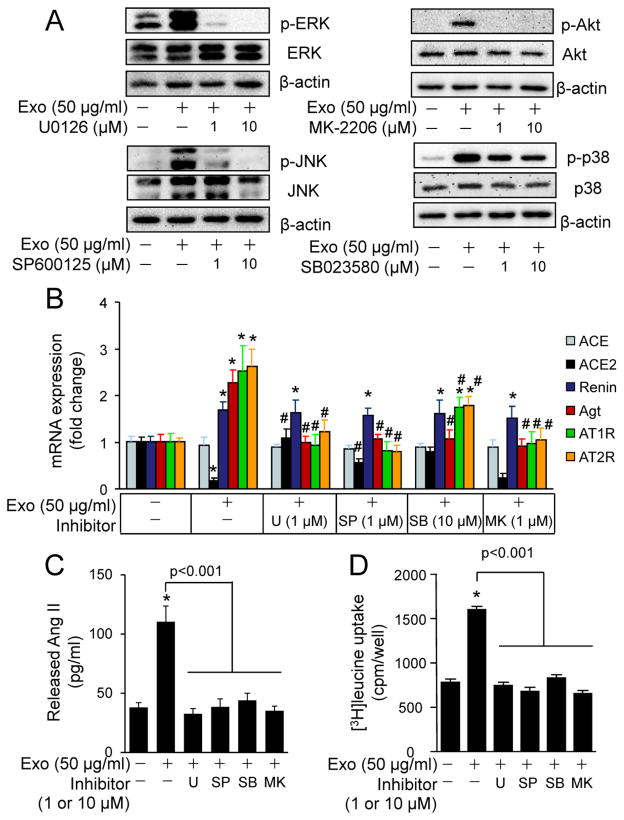
Fig. 6.
The effects of MAPK and Akt inhibitors on cardiac fibroblast-derived exosomes-induced activation of RAS in cardiomyocytes. (A) Dose response of MAPK and Akt inhibitors on cardiac fibroblast-derived exosomes (Exo)-induced activation of MAPKs and Akt. Neonatal rat cardiomyocytes were treated with or without Exo (50 μg/ml), U0126, SP600125, MK-2206, and SB023580 for 20 min and subjected to Western blot analysis. The results are from 4 separate experiments. (B) The effects of MAPK and Akt inhibitors on Exo-induced mRNA expression of RAS components. Neonatal rat cardiomyocytes were treated with or without Exo (50 μg/ml), U0126 (U, 1 μM), SP600125 (SP, 1 μM), SB023580 (SB, 10 μM), and MK-2206 (MK, 1 μM) for 48 h and then subjected to qPCR analysis of mRNA expression of ACE, ACE2, renin, angiotensinogen (Agt), AT1R, and AT2R. n=4, *p<0.05 vs. Control (−). #p<0.05 vs. Exo (+) group. (C) The effects of MAPK and Akt inhibitors on Exo-induced Ang II release. Neonatal rat cardiomyocytes were treated with or without Exo (50 μg/ml), U0126 (U, 1 μM), SP600125 (SP, 1 μM), SB023580 (SB, 10 μM), and MK-2206 (MK, 1 μM) for 48 h. Ang II was measured in the culture medium. n=4, *p<0.05 vs. Control (−). (D) The effects of MAPK and Akt inhibitors on Exo-induced [3H]-Leucine uptake. Neonatal rat cardiomyocytes were treated with or without Exo (50 μg/ml), U0126 (U, 1 μM), SP600125 (SP, 1 μM), SB023580 (SB, 10 μM), and MK-2206 (MK, 1 μM) for 48 h. n=4, *p<0.05 vs. Control (−).