Figure 1.
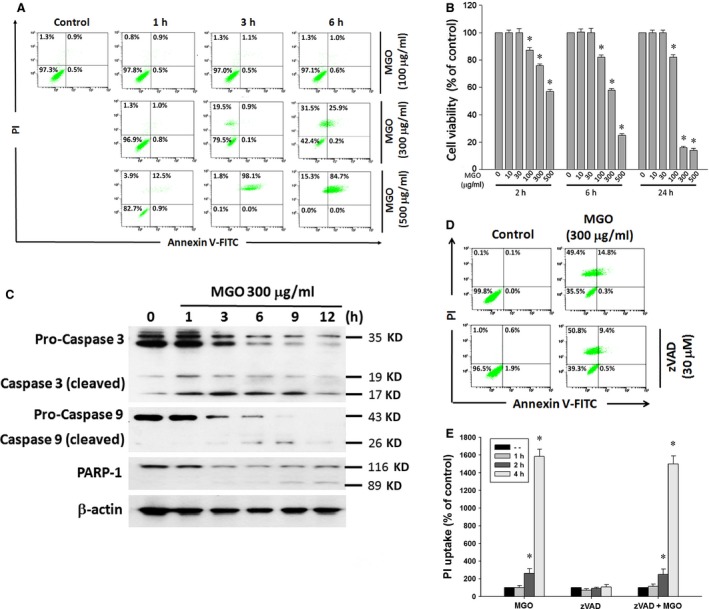
MGO decreases cell viability and induces caspase‐independent cell death in ARPE‐19 cells. (A) Cells were treated with various concentrations (100, 300 or 500 μg/ml) of MGO for 1, 3 or 6 h, and then stained with annexin V and PI, and evaluated by flow cytometry. (B) Cells were treated with various concentrations (10–500 μg/ml) of MGO for 2, 6 or 24 h. Cell viability was determined by MTT assay and the percentages of viability as compared to vehicle‐treated cells were plotted as the mean ± SE of at least three independent experiments. (C) Cells were treated with 300 μg/ml MGO for the indicated times. Cells were lysed and expression levels of indicated proteins were detected by Western blotting by using antibodies against caspase 3, caspase 9, PARP‐1 and β‐actin. (D) Cells were treated with pan‐caspase inhibitor zVAD (30 μM) for 30 min, followed by the treatment with 300 μg/ml MGO for 6 h. Cell viability was determined by annexin V/PI double staining assay. (E) After cells were treated with zVAD and MGO (300 μg/ml) for 1, 2 and 4 h, PI uptake was measured by flow cytometry. *P < 0.05, indicating the significant induction of cell death by MGO.
