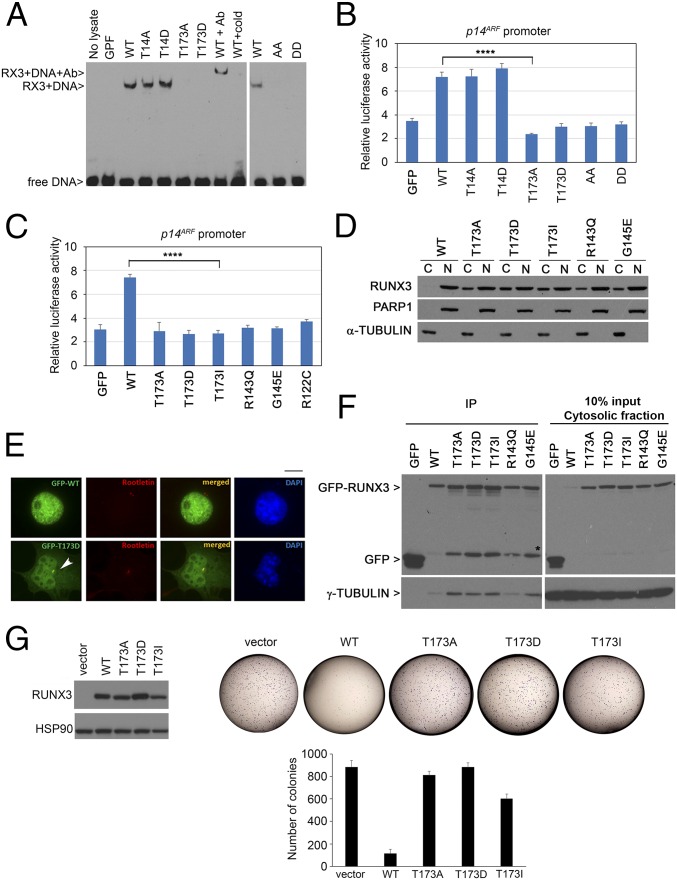
Fig. 4.
T173 mutants are impaired in DNA binding and transactivation properties. (A) DNA binding abilities of GFP-RUNX3 and phosphomutants. Nuclear extracts of the transfectants were analyzed by electrophoretic mobility assay using a DNA probe with the RUNX binding site. RUNX3 antibody (Ab) and nonbiotinylated probe (cold) were used for supershift reaction and competition assay, respectively. WT, wild type; GFP, empty GFP vector control; AA, T14A/T173A; DD, T14D/T173D mutants. (B) HEK293T cells were transfected with GFP-RUNX3 constructs, p14ARF promoter fused to firefly luciferase, and β-galactosidase normalization control. Mean values ± SDs are obtained from triplicate experiments. Comparison of WT and T173A, ****P = 0.00003 (Student’s t test). (C) Luciferase reporter assay of Runt domain mutants with the p14ARF promoter. Comparison of WT and T173I, ****P = 0.0001. (D) COS7 cells transfected with GFP-RUNX3 constructs were subjected to biochemical fractionation to isolate cytosolic fraction (C) and nuclear fraction (N). Immunoblot was done with GFP, PARP, and α-tubulin antibodies to detect RUNX3 and validate purity of the nuclear and cytosolic fractions, respectively. (E) GFP-RUNX3 (WT) and GFP-T173D were transfected into COS7 cells for fluorescence microscopy. Rootletin antibody indicated centrosome (red) while DAPI counterstained for DNA (blue), respectively. White arrow indicates centrosome. (Scale bar, 10 µm.) (F, Left,) Immunoprecipitation (IP) of cytosolic fraction in D using GFP beads. (Right) Cytosolic fraction. RUNX3 and bound γ-tubulin were detected by immunoblot with GFP and γ-tubulin antibodies. * indicates GFP-linked degradation products. (G, Left) Expression of pRetro-X-flag-RUNX3 constructs in HeLa Tet-On cells (induced with doxycycline) as detected by immunoblot with anti-flag antibodies. (Right) Colony formation assay of the stable cells at Left. Vector, empty vector control. Representative photographs are shown. The graph shows mean colony numbers ± SDs from three independent experiments.