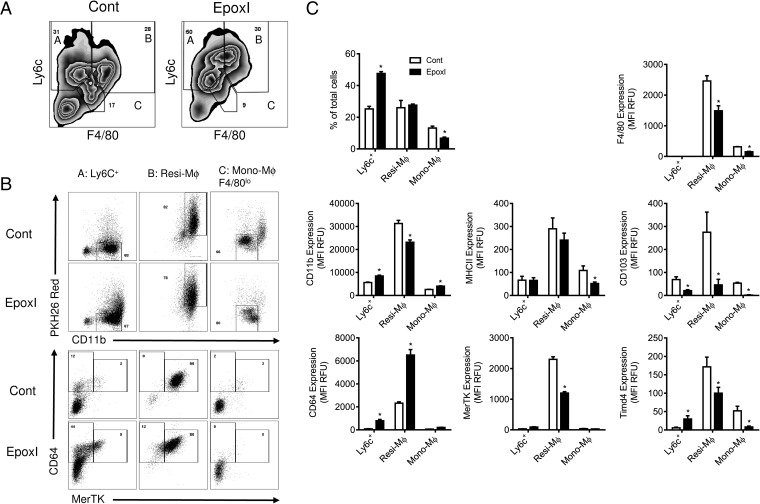
Fig. 6.
Epoxygenase inhibition regulates monocyte and macrophage differentiation. Inflammation was initiated by zymosan (1 mg, i.p.), and mice were treated with vehicle control (PBS) or epoxI (30 mg/kg, i.p.) at 24 and 36 h. Cells were collected at 48 h and pooled from n = 9–18 mice. Ly6c+ monocytes, resident macrophages, and monocyte-derived macrophages were sorted on a LSR Fortessa as detailed in Materials and Methods. (A) Representative zebra plots of the cell populations from control and epoxI-treated mice expressing Ly6c and F4/80, with labeled populations representing A: Ly6c+ monocytes; B: resident macrophages (Resi-Mϕ); and C: monocyte-derived macrophages (Mono-Mϕ). (B) Representative dot plots of the Ly6c+ monocytes, resident macrophages, and monocyte-derived macrophages from control and epoxI-treated mice expressing PKH26 and CD11b (Upper) and CD64 and MerTK (Lower). (C) Changes in cell numbers, and expression (MFI in relative fluorescence units; RFUs) for F4/80, CD11b, MHCII, CD103, CD64, MerTK, and Timd4 in the Ly6c+, Resi-Mϕ, and Mono-Mϕ cell populations. Data are mean ± SEM from n = 5 mice per group; *P < 0.05 by unpaired t test.