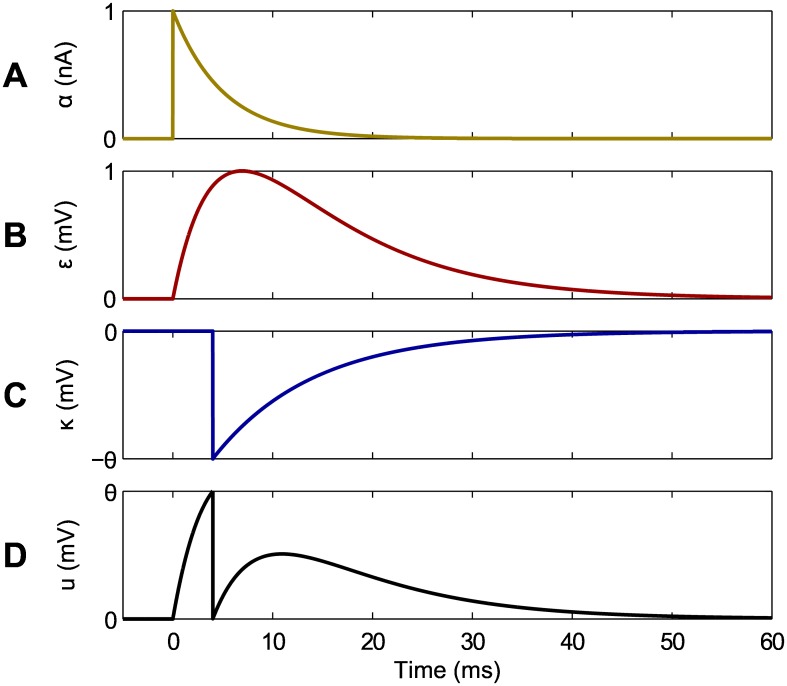
Fig 1. Illustration of the postsynaptic kernels used in this analysis, and an example of a resulting postsynaptic membrane potential.
(A) The time course of the postsynaptic current kernel α. (B) The PSP kernel ϵ. (C) The reset kernel κ. (D) The resulting membrane potential ui as defined by Eq (1). In this example, a single presynaptic spike is received at tj = 0 ms, and a postsynaptic spike is generated at ti = 4 ms from selectively tuning both the synaptic weight wij and firing threshold ϑ values. We take C = 2.5 nF for the neuron’s membrane capacitance, such that the postsynaptic current attains a maximum value of 1nA.