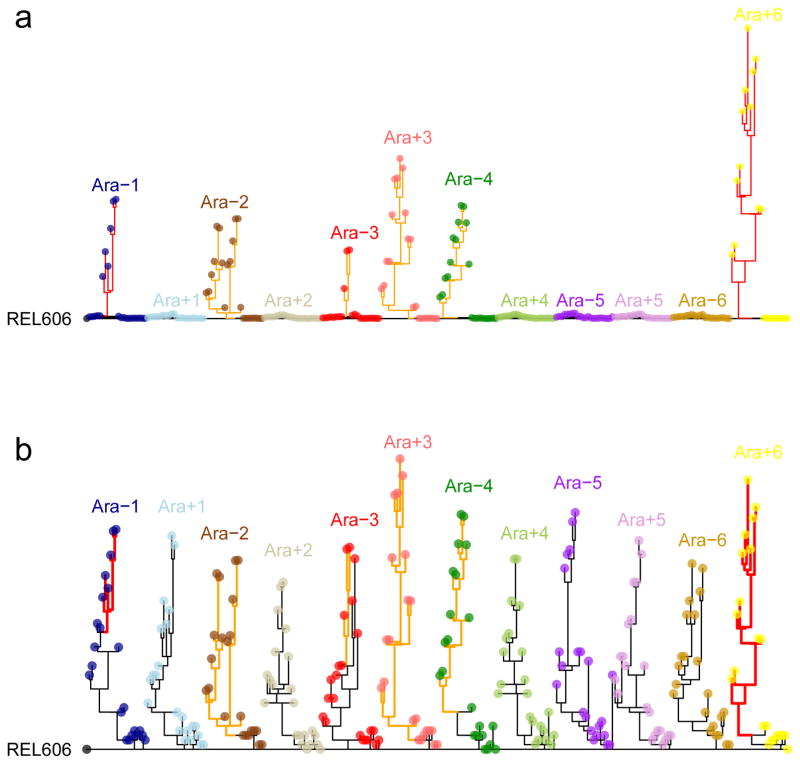
Figure 2. Phylogenetic trees for LTEE populations.
a, Phylogenies for 22 genomes from each population, based on point mutations. b, The same trees, except branches are rescaled as followed: branches for lineages with mismatch-repair defects are orange and shortened by a factor of 25; branches for mutT mutators are red and shortened by a factor of 50. Strain REL606 (at left) is the ancestor. No early mutations are shared between any populations, confirming their independent evolution. Most populations have multiple basal lineages that reflect early diversification and extinction; some have deeply divergent lineages with sustained persistence, most notably Ara −2.