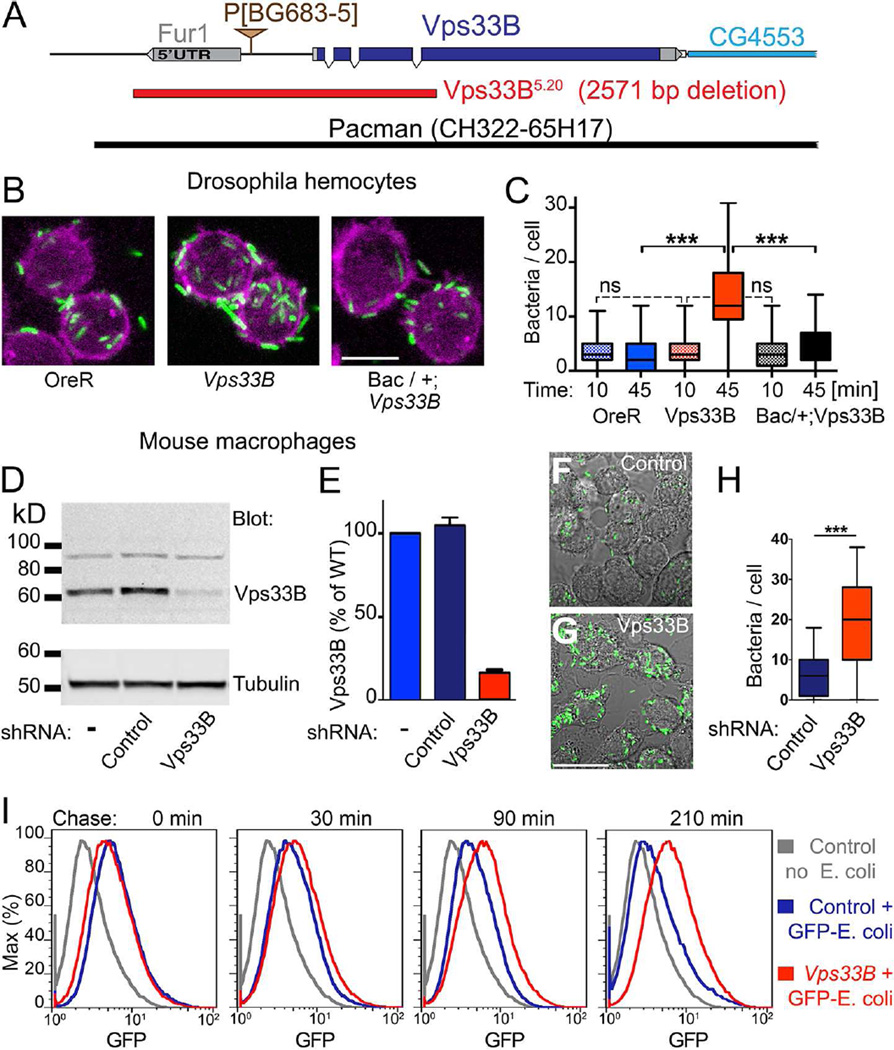
Figure 1. The requirement of Vps33B for phagosome maturation is conserved.
A) Map of Vps33B flanked by an alternative Fur1 noncoding exon and the neighboring CG4553 gene. The Vps33BB5.20 deletion allele removes the alternative Fur1 noncoding exon, the Vps33B promoter and codons for the first 196 amino acids of Vps33B. A transgene containing P[acman]Ch322-65H17 rescued all phenotypes of Vps33BB5.20 discussed here, but not a linked “blemished wing” phenotype.
B) Micrographs of primary hemocytes that phagocytosed GFP-labeled E. coli for 20 min and were chased for 45 min.
C) Quantification of phagocytosed E. coli detectable after 10-min or 45-min chases. Genotypes in B, C: were OreR, w1118;+/+;Vps33B5.20, and w1118; BACCH322-65H17/+; Vps33B5.20. (***: p<0.001, One way ANOVA)
D) Immuno blots of macrophages expressing none, scrambled control or Vps33B shRNA developed with Vps33B antibodies. Alpha-tubulin served as loading control.
E) Quantification of Vps33B protein from western blots as shown in D (n = 3).
F,G) Micrographs of macrophages expressing scrambled control (F) or Vps33B shRNA (G) allowed to phagocytose GFP-labeled E. coli for 20 min followed by a 45-min chase.
H) Quantification of phagocytosed E. coli detectable after a 45-min chase as shown in F and G (***: p<0.001, Two-tailed t-test).
I) Flow cytometry analysis of macrophages expressing control or Vps33B shRNA allowed to phagocytose GFP-labeled E. coli for 20 min followed by a chase of the indicated times. [All data here are representative of at least 3–5 independent experiments.
Please also see Figure S1.