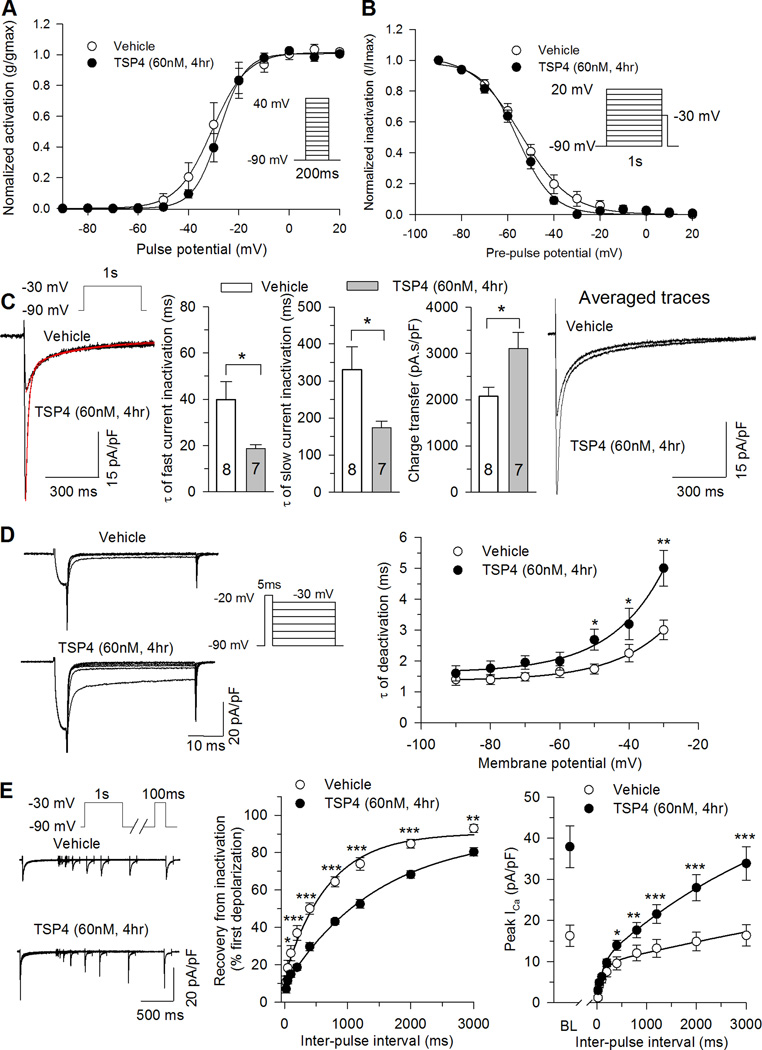
Figure 5. Effects of TSP4 on biophysical properties of LVA VGCCs.
TSP4 treatment did not change T-type ICa voltage dependence of activation (A, n = 8 Vehicle control, n = 7 TSP4). TSP4 treatment had no effect on steady state inactivation (B, n = 6 Vehicle control, n = 6 TSP4), but did accelerate inactivation (C, sample traces left panel, and summary data middle panel), including reduced τ for both the fast and slow components of inactivation, while total charge transfer was unaffected and average current density was still greater at all timepoints following the initiation of depolarization (C, right panel). TSP4 reduced the rate of recovery of LVA ICa from inactivation (D), but the average current density in TSP4-treated neurons is greater than vehicle controls at all timepoints during recovery (D, right panel, BL: baseline). TSP4 slowed deactivation of LVA ICa from activation (E, n = 7 Vehicle control, n = 7 TSP4). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, Tukey post hoc analysis following 2-way repeated measures ANOVA.