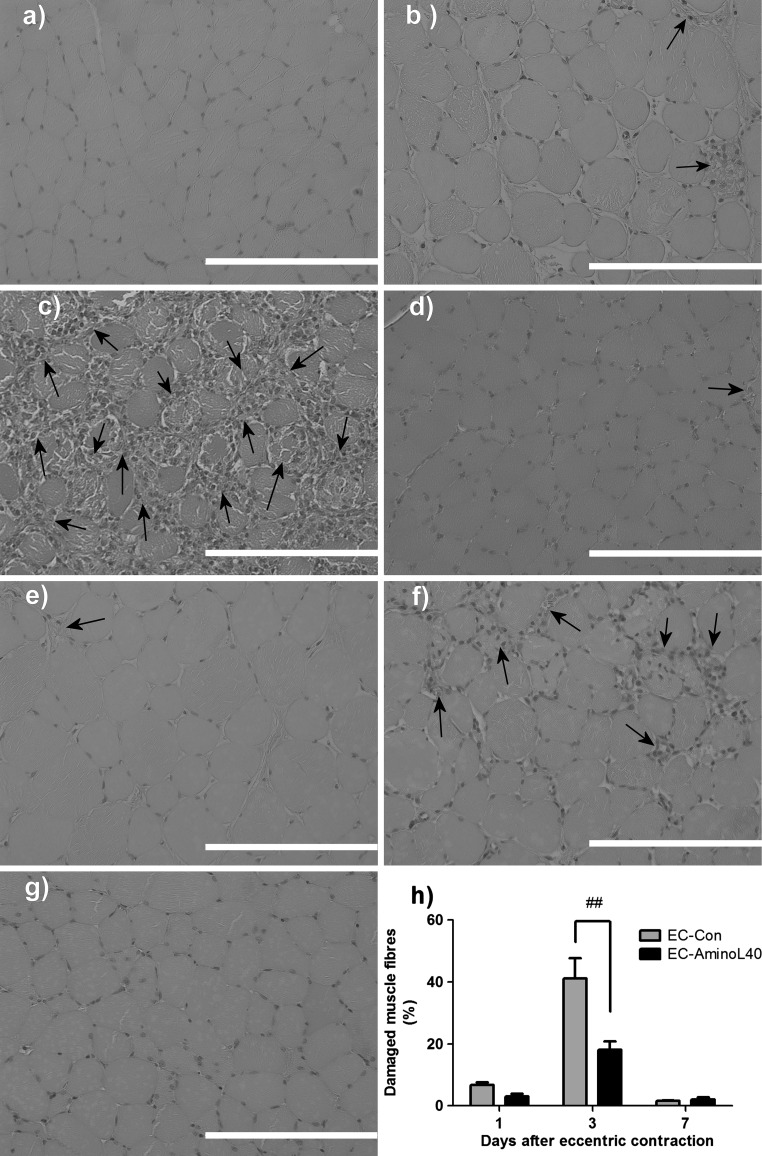
Fig. 4.
Histochemical analysis of the tibialis anterior muscle before and after eccentric contraction. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of transverse sections of the muscle in a sedentary animals (Sed), and from b–d rats that underwent eccentric contraction and received water (EC-Con) or e–g leucine-enriched essential amino acids (EC-AminoL40). Tissues were collected b, e 1 day, c, f 3 days, and d, g 7 days after eccentric contraction. Images are representative sections from 4–5 rats killed at a given time point, with magnification ×40. Scale bars 100 μm. h Muscle damage 1, 3, and 7 days after eccentric contraction, as assessed by point counting, and expressed as percentage of muscle fibers infiltrated with inflammatory cells (arrows) in each sampling grid. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 4–6). ##, p < 0.001