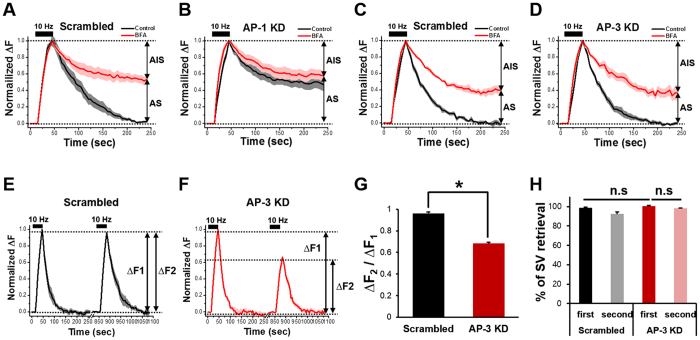
Figure 5. BFA-sensitive SVs are retrieved via AP-1/AP-3 dependent mechanisms.
(A–D) Hippocampal neurons were transfected with shRNAs targeted to AP-1 or AP-3 or respective scrambled shRNAs. At DIV14, neurons were stimulated with 300 APs at 10 Hz in the presence or absence of BFA, and average SypHy fluorescence intensity profile of the boutons was normalized to its peak value and plotted against time. Error bars indicate SEM. AP-1 sensitive SV (AS) = 49.0 ± 6.5%, AP-1 insensitive SV (AIS) = 51.0 ± 6.5% for AP-1 KD (AP-1 shRNA: n = 124 neurons from 14 independent coverslips for the scrambled, n = 89 neurons from 9 independent coverslips for AP-1 KD; AP-3 shRNA: n = 60 neurons from 7 independent coverslips for the scrambled, n = 73 neurons from 10 independent coverslips for AP-3 KD). (E,F) Average SypHy fluorescence intensity profiles of the boutons of the scrambled (black) or AP-3 knock-down (KD) neurons (red). The same group of neurons was stimulated with 300APs at 10 Hz twice and the change in fluorescence induced by the second stimulation (ΔF2) was normalized to that induced by the first stimulation (ΔF1). Error bars indicate SEM (n = 41 neurons from 5 independent coverslips for the scrambled, n = 28 neurons from 4 independent coverslips for AP-3 KD). (G) The ratio of ΔF2 over ΔF1. *p < 0.01 (Student’s t-test). (H) The percentage of SV retrieval over fusion after the first and second stimulation in the scrambled (black, grey) and AP-3 KD neurons (red, pink). Data are presented as means ± SEM.