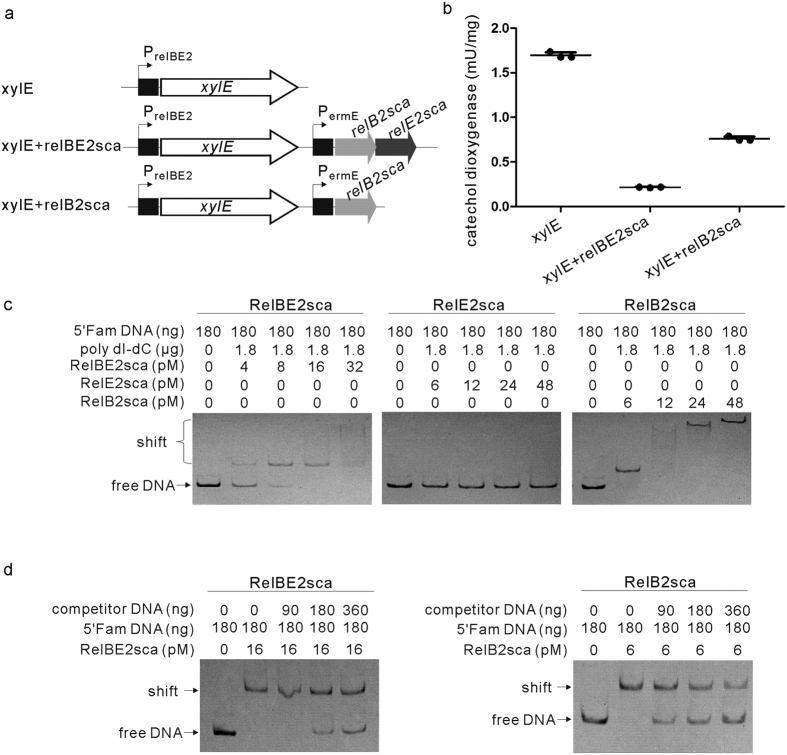
Figure 4. Auto-regulation of the S. cattleya relBE2sca operon by the RelBE2sca TA complex or the antitoxin RelB alone.
(a) Schematic representation of in vivo regulation of relBE2sca operon in S. lividans TK24 xylE, reporter gene coding for catechol 2,3-dioxygenase; PrelBE2, promoter region of S. cattleya relBE2sca; PermE, strong constitutive promoter. (b) Activity of catechol 2,3-dioxygenase was assayed by monitoring the increase in absorbance at 375 nm (A375) every 10 minutes for the S. lividans TK24 cells carrying the resulting plasmids. (c) Analysis of the interactions between PrelBE2 and RelBE2sca proteins by using EMSA in vitro. Increasing the amount of RelBE2sca-His6, RelE2sca-His6 or RelB2sca was incubated with the promoter labeled with 5′-FAM. Poly dI-dC was used to inhibit the unspecific interaction. Unbound DNA fragments were separated from protein-DNA complex by electrophoresis in 6% native PAGE gel. (d) Increasing amounts of unlabeled competitor DNA were added into the reaction system in which the amounts of His6-RelBE2sca complex or RelB2sca were set at 16 pM or 6 pM, respectively.