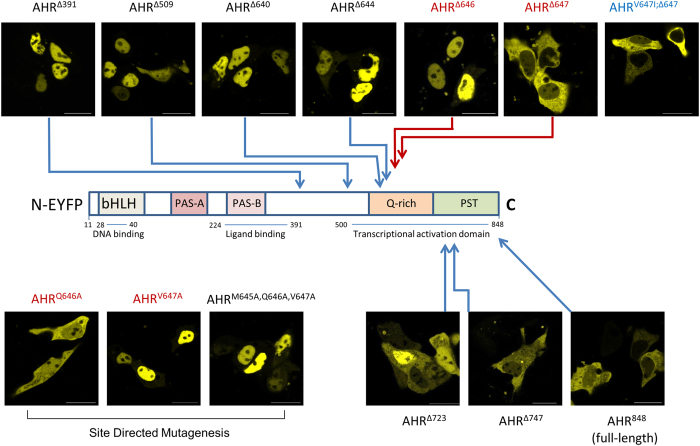
Figure 2. V647 determines the compartmentalisation of the AHR: expression of fluorescent AHR deletion mutants in HepG2 cells.
Deletion mutants were derived from full-length human pEYFP-AHR-C1 (AHR848). Mutants are named according to truncations sites, as defined by the last included residue. These sites are marked on the drafted full-length protein. Representative images that reflect the typical compartmentalisation are shown (scalebar = 20 μm). Mutants truncated after amino acid 391 (AHR∆391), 509 (AHR∆509), 640 (AHR∆640) 644 (AHR∆644) and 646 (AHR∆646) show an exclusive nuclear staining, whereas the full-length protein (AHR848) is predominantly located in the cytosol. AHR∆647 is nearly exclusively detected in the cytoplasm. Inclusion of the Q-rich domain does increase nuclear association (AHR∆723). This is balanced by a motif localised between Pro 728 and Leu 744 within in the PST domain. AHR∆647 and full-length AHR848 show a similar predominantly cytoplasmic localisation. Replacing of residues M645, Q646 and V647 (AHRM645A,Q646A,V647A), or V647 only (AHRV647A) by alanines led to an exclusive nuclear staining, whereas mutant AHRQ646A showed wild-type compartmentalisation (lower panel left). On the other side, replacement of V647 with isoleucine (AHRV647I;∆647) did not affect the cytoplasmic staining pattern (upper panel right).