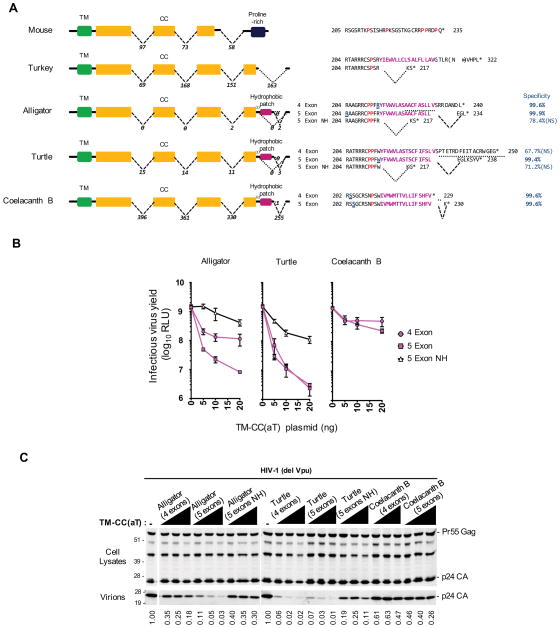
Figure 6. Antiviral activity of non-mammalian TM-CC(aT) variants.
(A) Transcript structure and C-terminal protein sequences of potential alternatively spliced isoforms of tm-cc(at) in non-mammalian species. The TM, CC and proline-rich domains and hydrophobic patch are indicated in color. The omega site (underlined in blue) and specificity (1 – false positive rate) were predicted using PredGPI. The number of RNAseq reads supporting the occurrence or absence of splicing events are indicated between the exons.
(B) Infectious virion yield measured using HeLa TZM-bl indicator cells following transfection of Vpu-deficient HIV-1 proviral plasmids along with plasmids expressing alternatively spliced isoforms of TM-CC(aT) proteins. NH= no hydrophobic (isoforms lacking the hydrophobic patch). (RLU= relative light units, Mean ± SD, n=3).
(C) Western blot analyses (anti-CA) of cell lysates and virions corresponding to (B). Numbers at the bottom represent virion CA protein levels relative to those obtained in the absence of an inhibitor.
See also Figure S6.