Fig. 8.
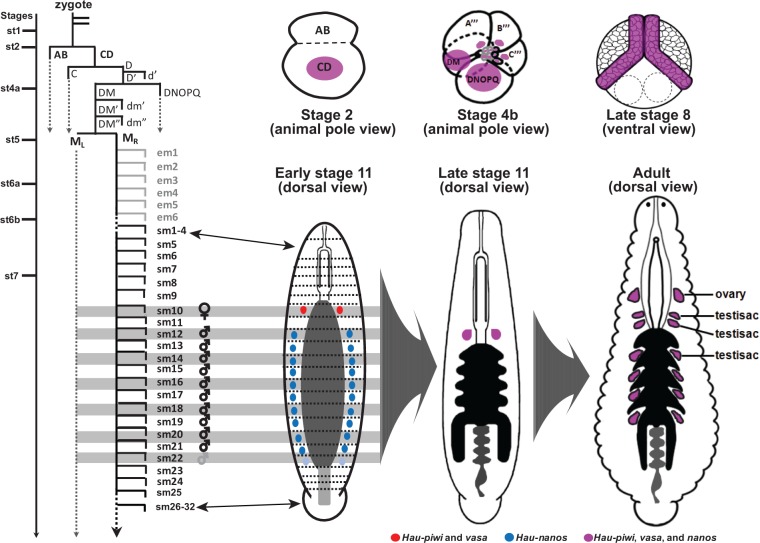
Diagrammatic summary of germ line marker expression and PGC segregation in Helobdella. Lineage diagram depicting cell divisions leading from the zygote to the segmental founder cells from which female and male PGCs arise, with line drawings showing the expression of conserved germ line markers at selected stages and in the adult leech (nanos, blue; coexpression of piwi and vasa red; coexpression of nanos, piwi and vasa, purple). Time line is approximate: from zygote to stage 7 takes about 54 h at 23 ° C; teloblast cell cycles are 1–2 h. Bilateral M teloblasts arise at seventh cleavage from the division of DM″ (micromere 4d in standard nomenclature for spiralian embryos); each M teloblast undergoes six further rounds of stem cell division that produce nonsegmental early mesoderm blast cells (em1–em6) before producing its first segmental blast cell (sm1, corresponding to segment R1) (Gline et al. 2011); finally, nine further rounds of mitosis occur before the precursors of the female germ line (sm10, segment M6) are separated from the precursors of the male germ line (which arise from the M teloblast starting with sm12, segment M8). As shown in figure 3C, coexpression of all three markers is prominent in teloplasm and teloblast precursors (but is also seen in other cells) during cleavage stages (e.g., stages 2 and 4b), and in the germinal bands and early germinal plate (stage 8). By early stage 11, expression of piwi and vasa has become restricted to the females PGCs (segment M6), whereas nanos is restricted to prospective male PGCs (segments M8–M17 in H. austinensis; and also segment M18 in H. robusta, indicated by paler shading). By late stage 11, expression of all three genes is restricted to the female PGCs. The point at which expression resumes in adult male PGCs remains to be determined. See text for further details. In the adult, ovaries are associated with segment M6 and definitive testisacs with segments M8–M13.