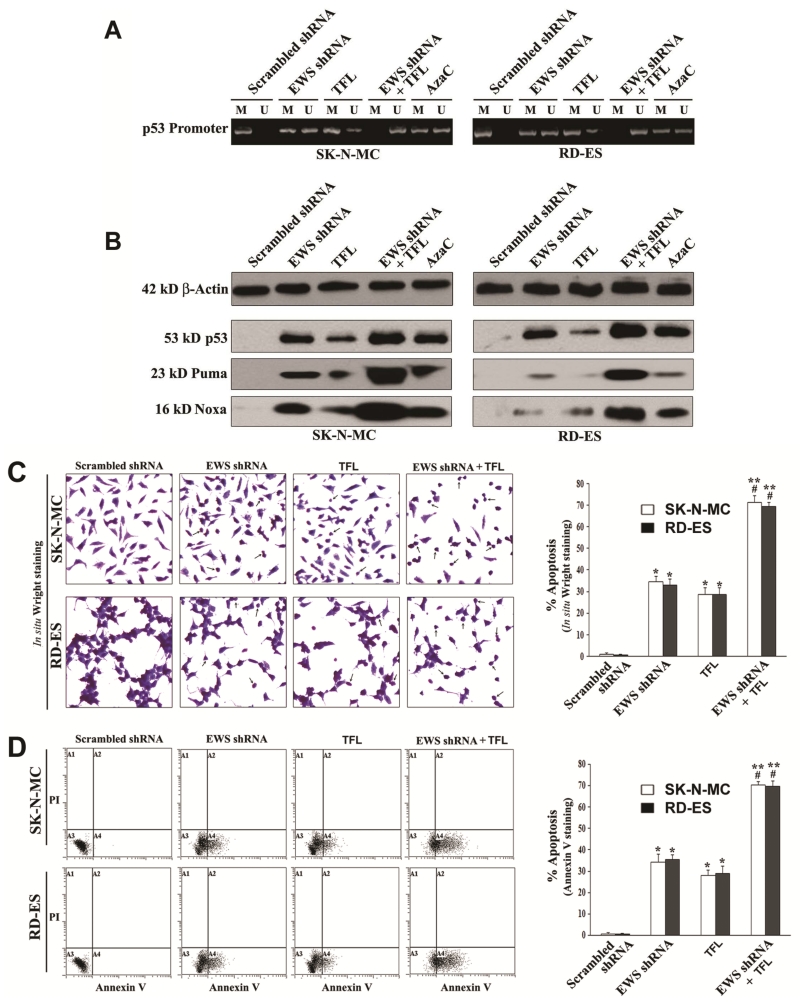
Figure 6.
Decrease in DNA methylation at the p53 promoter region promoted apoptosis in human Ewing’s sarcoma SK-N-MC and RD-ES cell lines. Treatments: scrambled shRNA plasmid (0.5 μg/ml) transfection for 72 h, EWS shRNA plasmid (0.5 μg/ml) transfection for 72 h, 100 μM TFL treatment for 24 h, EWS shRNA palsmid (0.5 μg/ml) transfection for 48 h + 100 μM TFL treatment for last 24 h, and 5 μM AzaC for 72 h. (A) MSP analysis of the p53 gene promoter region. The bisulfite-treated genomic DNA samples were used for MSP amplification of the human p53 promoter region using the MSP primers specific for either methylated (M pair) or unmethylated (U pair) DNA. (B) Western blotting to examine expression of the tumor suppressor protein p53 and the pro-apoptotic proteins Puma and Noxa. (C) In situ Wright staining for detection and determination of morphological features of apoptosis. (D) Annexin V-FITC/PI staining followed by flow cytometery for detection and determination of a biochemical feature of apoptosis. Mean values (n = 3) were shown and significant difference between two values was indicated by *P < 0.05 or **P < 0.01 (where monotherapy or combination therapy was compared with scrambled shRNA) and #P < 0.01 (where combination therapy was compared with monotherapy).