Figure 2. Aqueductal obstruction. A–D: Aqueductal obstruction associated with L1CAM mutation.
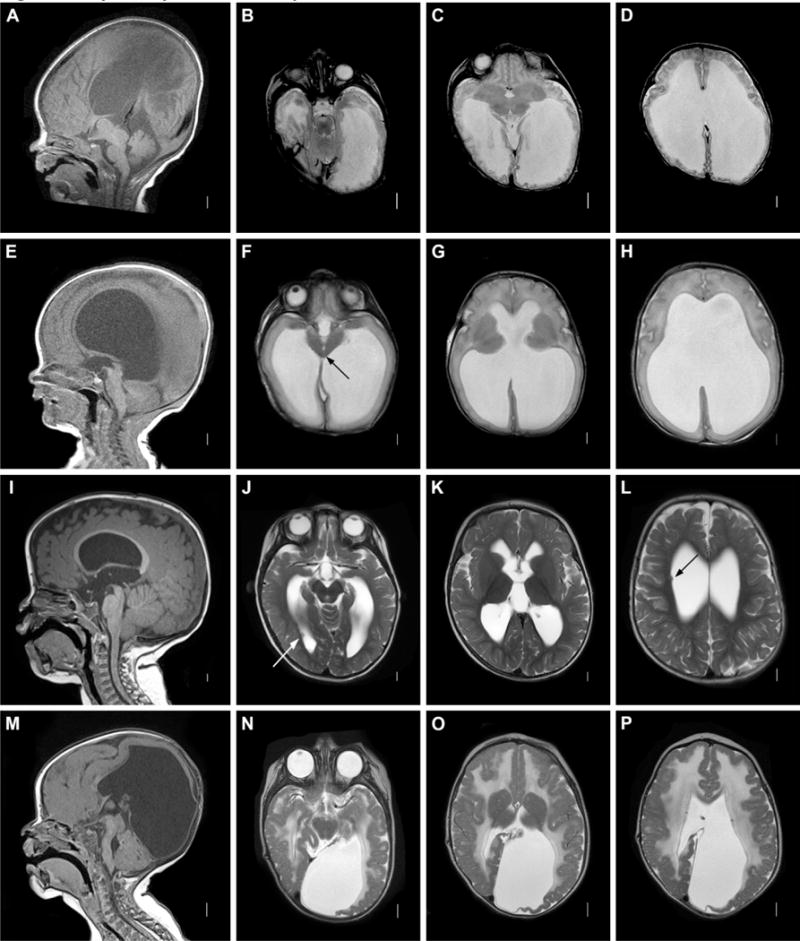
Sagittal T1 MRI image (A) showing complete aqueductal occlusion (arrow) and small cerebellum. Axial T2 images (B–D) demonstrating extensive dilation of lateral ventricles. E–H: Mesencephalosynapsis. Sagittal T1 images (A) demonstrating inferior aqueductal occlusion with funneling (arrow). Axial T2 images (F–H) showing fused inferior colliculi (arrow) and severe ventricular dilatation. I–L: Periventricular nodular heterotopia with aqueductal nodule. Sagittal T1 image (A) showing obstructive nodule within aqueduct (arrow). Axial T2 images (J–L) demonstrating moderate ventricular dilatation and periventricular nodular heterotopia (arrows.) M–P: Muscle-Eye-Brain disease. Sagittal T1 image (M) showing enlarged tectum with complete aqueductal obstruction (arrow), hypoplastic and kinked brainstem, and cerebellar dysplasia with cysts. Axial T2 images (N–P) showing cobblestone cortex and abnormal white matter.
