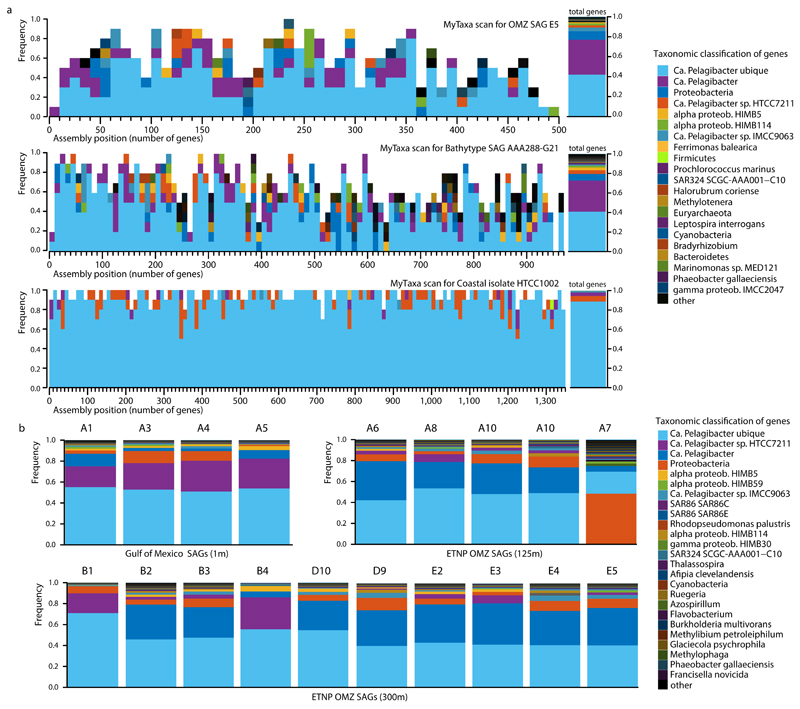
Extended Data Figure 1. Evaluation of contamination based on MyTaxa taxonomic affiliations.
a, Representative MyTaxa plots to test for contamination based on taxonomic affiliations of predicted genes. The MyTaxa algorithm 51 predicts the taxonomic affiliation based on a weighted classification scheme that takes into account the phylogenetic signal of each protein family. Each gene is assigned to the deepest taxonomic resolution (out of phylum, genus, and species) for which a high confidence value can be obtained (score 0.5). Each MyTaxa scan represents taxonomic distributions of all the predicted genes for one genome, given in windows of 10 genes, and sorted based on their position in the concatenated assembly of the genome (when a partial genome is used). White space in the histograms represents genes that could not be assigned to a given taxon due to (a) lack of BLASTP hits against the reference database (a collection of closed and draft genomes) or (b) lack of high confidence scores. Notice that for the representative OMZ SAG E5, more than 80% of the genes can be classified as Candidatus Pelagibacter (SAR11), with an additional 10% assigned to Proteobacteria. Note there are no genome representatives for this taxon (i.e., SAR11 subclade IIa.A) in the database upon which MyTaxa is based. Similar results are obtained for the bathytype SAR11 SAG 6, as this genome also lacks representatives. The closed genome from a coastal isolate HTCC1002 is shown for comparison to demonstrate a typical pattern for cases when close relatives of the query genome are available in the reference database, as is the case for this isolate. b, Taxonomic classifications of genes from the 19 SAGs analyzed here. Each distribution was obtained from the MyTaxa scans performed for each SAG. The percentage of the total genes that could be taxonomically classified with MyTaxa was on average ~60%, and varied depending on the completeness of the genome (i.e., partial genes are less likely to be assigned taxonomy with high confidence). These values are also reported in Supplementary Table 1. Of the genes that could be classified, the majority (>90%) were classified to SAR11 taxa.