Figure 4.
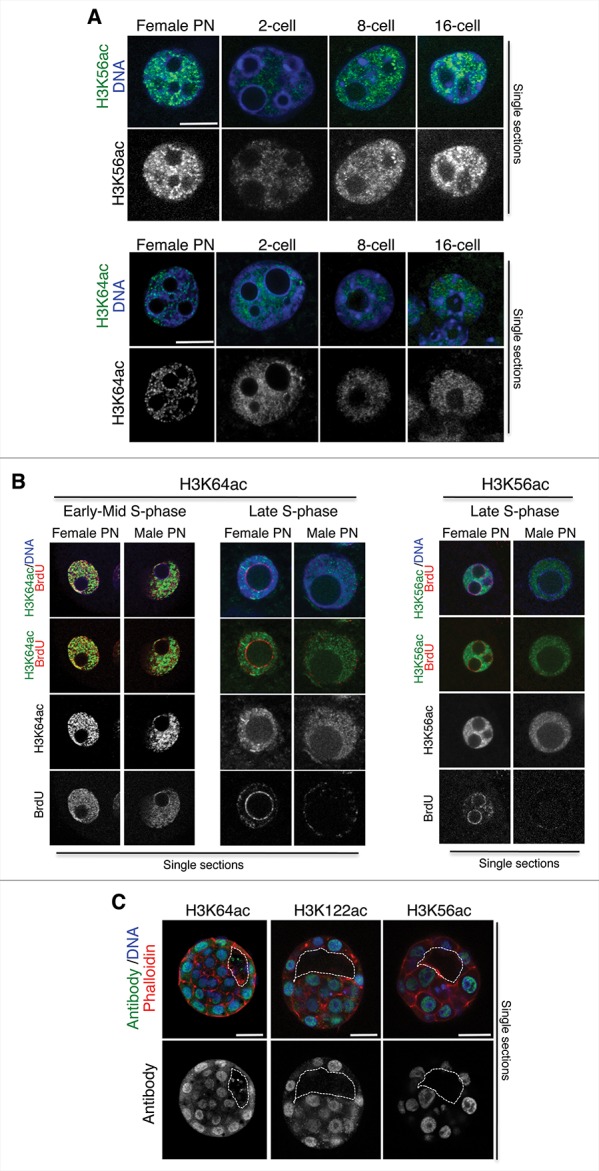
Relationship between H3K56ac or H3K64ac and S-phase progression. (A) Higher magnification of a representative female pronucleus or nuclei from 2-, 8-, or 16-cell stage embryos stained with the H3K56ac or the H3K64ac antibody. Shown are merge images of single confocal sections. Scale bar is 12 μm. (B) Zygotes were subjected to a BrdU pulse for 30 min during early/mid or late S-phase and processed for immunostaining with an anti-BrdU and an anti-H3K64ac (left) or an anti-H3K56ac (right) antibody. Representative zygotes of 10 analyzed at different stages of S-phase derived from 3 (H3K56ac) or 2 (H3K64ac) independent experiments are shown. Note, that the late replication pattern is characterized by BrdU incorporation at the satellite sequences around the NLBs and remaining BrdU at the peripheral nuclear regions. Shown are single sections of Z-stack sections taken every 0.5 μm where the diameter of the male pronucleus is maximal. Male and female pronuclei are shown. Scale bar is 12 μm. (C) Middle section of an early blastocyst stained with the H3K64ac, the H3K122ac, or the H3K56ac antibody. Shown are the merge images of the green (antibody), blue (DAPI), or red (cortical actin stained with phalloidin) channels. The white line delineates the blastocyst cavity. Scale bar is 20 μm. Representative embryos from 8, 9, or 12 embryos for the H3K64ac, H3K122ac, and H3K56ac antibodies are shown.
