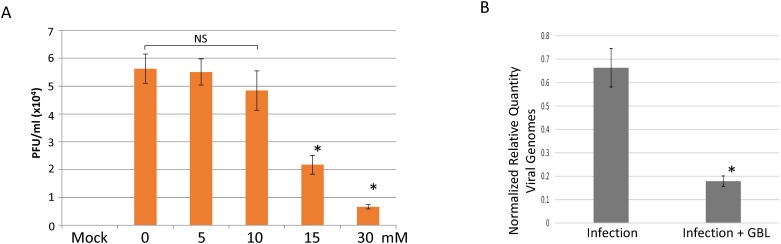
Fig 7. Concentration-dependent effects of GBL on viral replication.
A. The replication was determined by plaque assays (PFU/ml) using media to measure the release of infectious virus particles. Different concentrations of GBL ranging from 5-30mM were used. A statistical examination was done by ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-hoc test. Bars marked with an asterisk (*) were shown to be statistically significant in comparison to no GBL control with a p<0.05. NS: not significant with p>0.05. B. Total DNA was isolated followed by a quantitative PCR measuring virus genome via the method of Normalized Relative Quantity (NRQ). A statistical investigation was executed using Student's t-tests. Bars marked with an asterisk (*) were shown to be statistically significant in comparison to the infection control with a p<0.05.