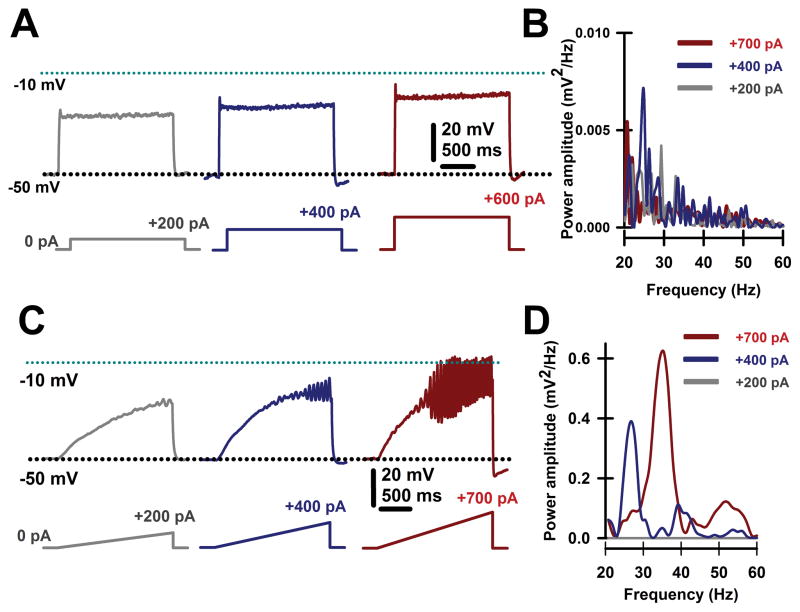
Figure 3. Intrinsic membrane oscillations in PPN neurons.
A. Recordings were performed in the presence intracellular high potassium solution and extracellular fast synaptic blockers and sodium channel blockers to study only intrinsic membrane properties. Square steps of increasing current levels depolarized the membrane but failed to induce clear high frequency oscillations. B. Overlapping power spectra amplitudes for oscillations obtained using steps shown in A. Power spectra were obtained using a Hamming window function after 20–60 Hz bandpass filtering oscillations generated by the depolarizing steps. Note the absence of beta/gamma frequency membrane oscillations. C. Recordings performed as in A, except using depolarizing ramps of similar currents. Ramps were able to sufficiently depolarize the membrane to induce robust oscillations, later confirmed to be due to high threshold, voltage-dependent calcium channels. D. Overlapping power spectra amplitudes for oscillations obtained using ramps shown in C. Power spectra were obtained using a Hamming window function after 20–60 Hz bandpass filtering oscillations generated by the depolarizing ramps. Note the presence of beta/gamma frequency membrane oscillations.