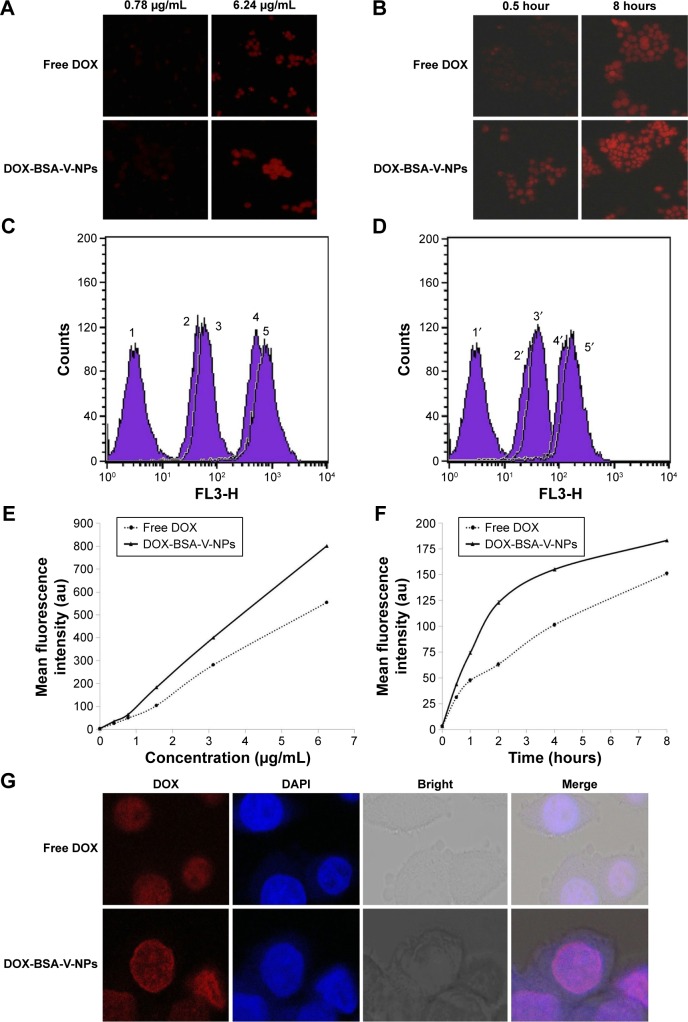
Figure 7.
Cellular uptake of free DOX and DOX-BSA-V-NPs.
Notes: Cellular internalization of free DOX and DOX-BSA-V-NPs observed by (A, B) inverted fluorescence microscopy (100× magnification), (C–F) flow cytometry, and (G) CLSM (400× magnification). (C) 1, control; 2, free DOX (0.78 μg/mL, 2 hours); 3, DOX-BSA-V-NPs (0.78 μg/mL, 2 hours); 4, free DOX (6.24 μg/mL, 2 hours); 5, DOX-BSA-V-NPs (6.24 μg/mL, 2 hours). (D) 1′, control; 2′ free DOX (1.56 μg/mL, 0.5 hours); 3′, DOX-BSA-V-NPs (1.56 μg/mL, 0.5 hours); 4′, free DOX (1.56 μg/mL, 8 hours); 5′, DOX-BSA-V-NPs (1.56 μg/mL, 8 hours). (E) Concentration-dependent uptake of free DOX and DOX-BSA-V-NPs. The cells were exposed to various concentrations of the DOX formulations at 37°C for 4 hours, and subsequently determined by flow cytometry. (F) Time-dependent uptake of free DOX and DOX-BSA-V-NPs. The cells were treated with the DOX formulations at a concentration of 1.56 μg/mL at 37°C and then analyzed by flow cytometry. (G) DOX (1.56 μg/mL, 4 hours) and DOX-BSA-V-NPs (1.56 μg/mL, 4 hours).
Abbreviations: BSA, bovine serum albumin; CLSM, confocal laser scanning microscopy; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; DOX, doxorubicin; NPs, nanoparticles; V, vanillin.