Figure. 2.
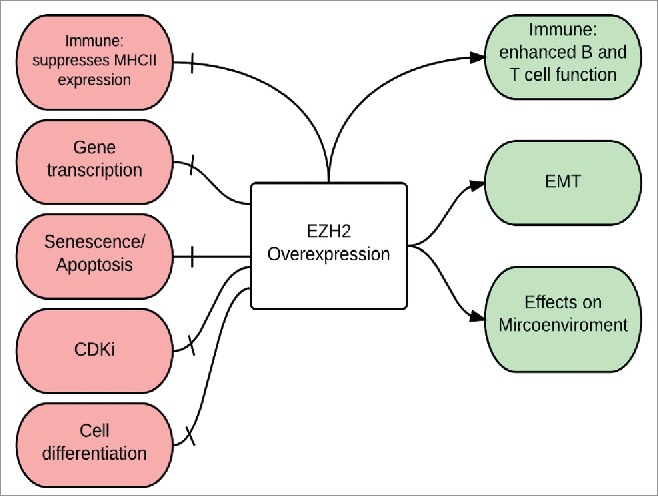
Biology of EZH2 overexpression in melanoma The Immune system: EZH2 overexpression has a positive effect on the immune system by enhancing the function of both B and T cells, however, it has a negative effect by suppressing MHC II expression and hence help melanoma cells escape immune surveillance; Gene transcription: EZH2 silences tumor suppressor genes; Senescence and apoptosis: EZH2 silences apoptotic genes and helps melanoma cells escape senescence; CdKI: EZH2-mediated silencing of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (CdkI), also called INK4 proteins, results in inhibition of apoptosis and senescence and stimulation of melanoma cell proliferation; Cell differentiation: EZH2 enhance the process of de-differentiation to neural-like stem cells; Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) and Microenvironment: EZH2 regulates the EMT and causes morphologic changes in melanocytes (increased motility, branching, aggressive growth, and cell migration) that help shape the interactions between melanoma cells and the microenvironment.
