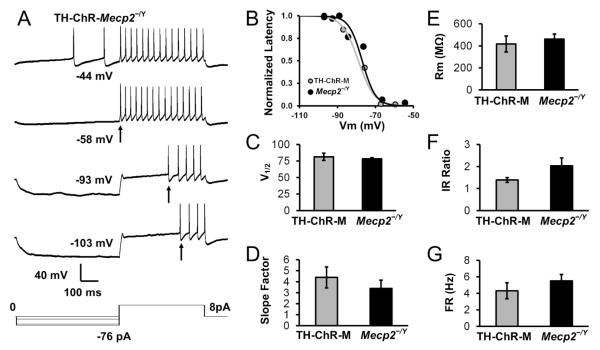
Fig. 4. Electrophysiological properties of LC neurons.
A. Whole cell current clamp recording from an LC neuron TH-ChR-Mecp2−/Y (TH-ChR-M) mice. The LC neuron showed delayed excitation (DE) with a series of hyperpolarizing steps followed by a depolarizing pulse. Step increases in hyperpolarization elongated the delay of the first spike (indicated by arrows). B. The relationship between action potential delays and the conditioning membrane potentials was fitted with the Boltzmann equations in TH-ChR-M and Mecp2-null mice and plotted. C-D. There was no difference in the V½ and slope factor between TH-ChR-M mice (n=4 cells/2 mice) and Mecp2-null (n=5 cells/3 mice). E-G. There was no significant difference in input resistance (P = 0.606 unpaired t-test), inward rectification (P = 0.166, unpaired t-test), and firing rate (P = 0.361, unpaired t-test) between TH-ChR-M mice (n=4 cells/2 mice) and Mecp2-null (n=5 cells/3 mice).