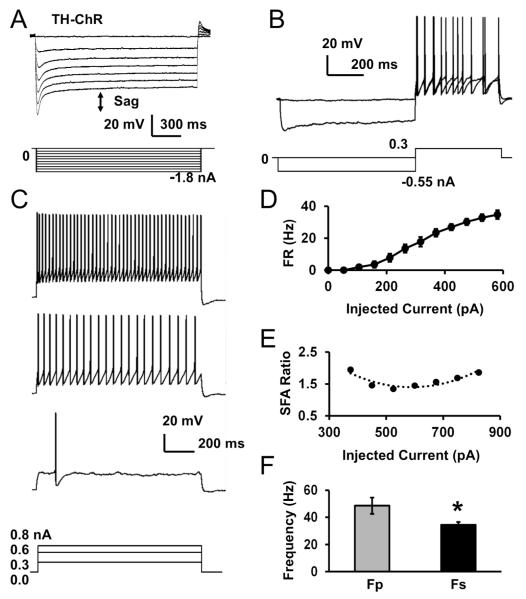
Fig. 5. Electrophysiological properties of hypoglossal neurons (HNs) from TH-ChR mice.
A. An HN was recorded in current clamp. The cell showed typical sag potential described as the voltage difference between the peak and steady-state voltages in response to steps of hyperpolarizing pulses (indicated with the arrow). The cell also displayed a post-inhibitory rebound of depolarization, which is the difference between the baseline and rebound voltage, after termination of hyperpolarizing pulses. B. The HN did not show DE. C. Increased firing activity and SFA was seen in the cell with depolarization currents. D. The average firing rate was calculated and graphed with depolarizing current injections, n=9 cells/2 mice. E. A moderate SFA ratio was seen in the HN. F. Fp and Fs were compared, n=9 cells/2 mice. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (*, P<0.05; Student’s t-test).