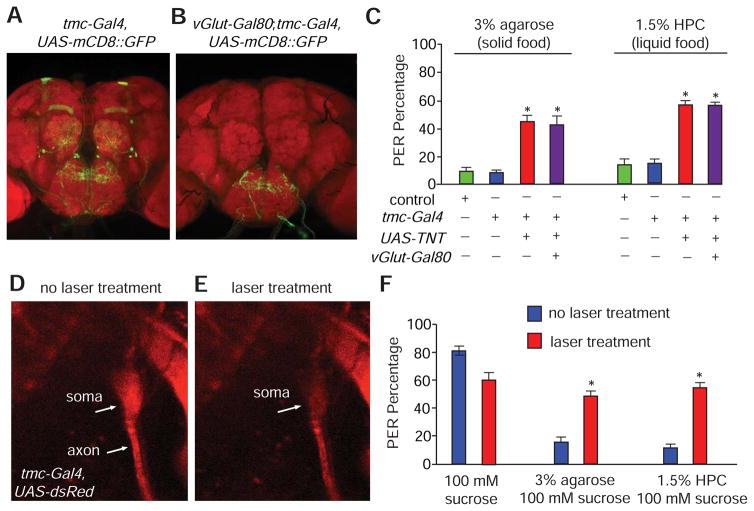
Figure 6. Requirements for md-L neurons for sensing food hardness and viscosity.
(A and B) Intersectional genetic labeling of the central projections of md-L neurons.
(A) Central brain expression pattern of tmc-Gal4,UAS-mCD8::GFP.
(B) Central brain expression pattern of tmc-Gal4,UAS-mCD8::GFP;vGluT-Gal80.
(C) PER responses to foods containing 100 mM sucrose plus either 3% agarose or 1.5% HPC. Shown are the responses of controls and flies expressing the indicated transgenes. n=20.
(D and E) Images showing the soma and axon of an md-L neuron (tmc-Gal4,UAS-DsRed).
(D) Prior to laser treatment.
(E) After laser treatment.
(F) PER responses to foods containing 100 mM sucrose and either 3% agarose or 1.5% HPC before and after md-L neurons were exposed to laser treatments. n=15.
The error bars indicate SEMs. *p<0.05. ANOVA tests with Scheffé’s post-hoc analysis.