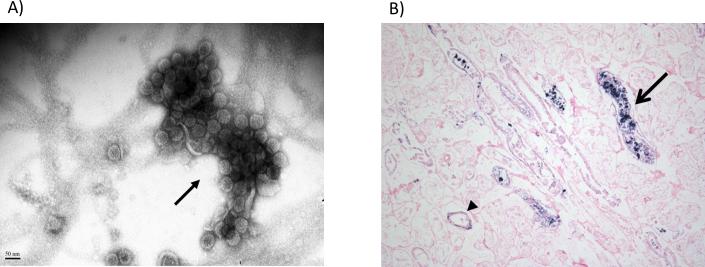
Figure 1. Polyomavirus nephropathy after hematopoietic cell transplant.
A) By routine electron microscopy (negative staining), a large polyomavirus Haufen (resembling a cast, arrow) is detected in a voided urine sample from a hematopoietic cell transplant recipient. B) Kidney autopsy specimen from a hematopoietic cell transplant recipient with detectable urinary polyomavirus Haufen. Tissue stained for BK virus using DNA in situ hybridization. Although the tissue is autolyzed, kidney tubules (arrow head) and tubular lumens (arrow) show positive staining for BK virus infected cells, defining polyomavirus nephropathy.