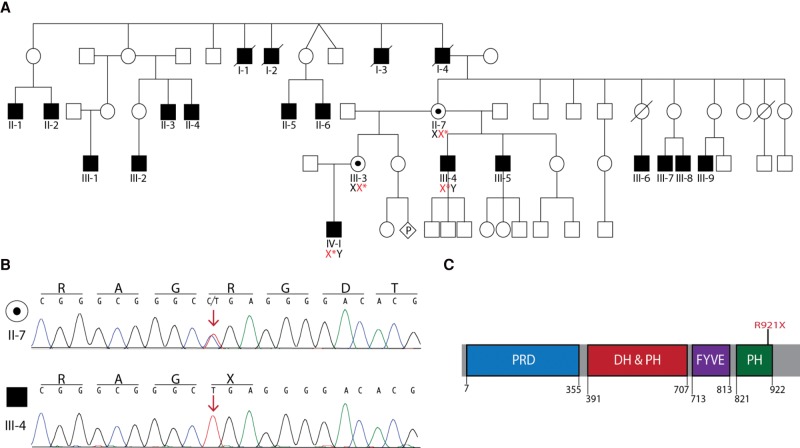
Figure 2.
Identification of a FGD1 mutation that segregates with phenotypic characteristics of Aarskog–Scott syndrome (AAS). (A) Pedigree of the affected family. DNA samples from the proband (IV-1) and his maternal uncle (III-4) were used for whole-exome sequencing. Sanger sequencing of Individuals IV-1 and III-4 confirmed the presence of the FGD1 mutation c.2761 C>T (red X*) in affected individuals and determined carrier status for Individuals II-7 and III-3. Empty symbols indicate unaffected individuals, filled symbols indicate affected individuals, and black dots indicate unaffected mutation carriers. Diamond-shaped symbol with a “P” represents unknown sex of a fetus in utero and slashes through symbols indicate deceased individuals. (B) Representative traces from Sanger sequencing confirming the presence of the c.2761 C>T mutation in an unaffected carrier female (II-7) and an affected male (III-4). Red arrow marks the affected nucleotide. The single-letter abbreviations for the nucleotides and corresponding amino acid codes are provided along the top of each trace. (C) Protein cartoon illustrates the known FGD1 functional domains in blue (proline-rich domain; PRD), red (DBL homology domain and pleckstrin homology domain; DH and PH), purple (FYVE zinc finger domain; FYVE), and green (pleckstrin homology domain; PH). The numbers indicate the amino acid positions for each domain. The position of the FGD1 R921X affected residue is indicated in red.