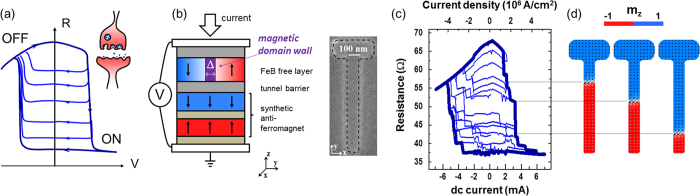
Figure 1. Spin-torque memristor.
(a) Typical resistance versus voltage cycles characteristic of a memristor. Inset: sketch of a biological synapse. (b) Side view: Schematic of our MgO based magnetic tunnel junction with the domain wall in the FeB free layer. Δ is the width of the domain wall. Top view: Scanning electron microscope image of the sample, with a black dashed line to emphasize its contour. (c) Resistance as a function of the vertically injected dc current (swept in the same direction than the one shown by the arrows in Fig. 1(a)), measured at an external field Hz = 85 Oe. (d) Micromagnetic simulations of the domain wall propagating in a magnetic track of 100 nm width. The tilt angle of the spin in the domain wall structure shows that for this width, the domain wall is hybrid between Neel and Bloch configurations.