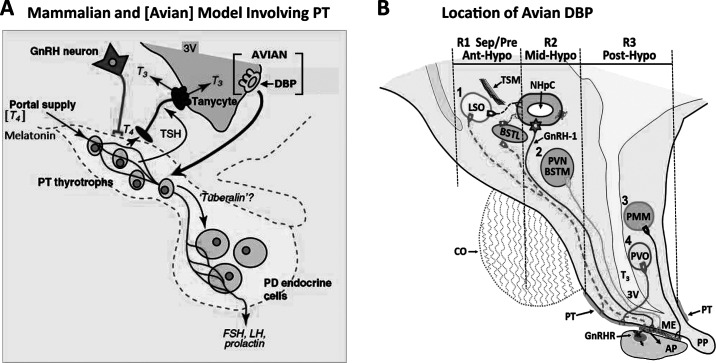
Figure 2.
A. Unifying model for pars tuberalis (PT)-dependent photoperiodic regulation of seasonal endocrine function in mammals and birds. Within brackets are deep brain photoreceptors (DBP) found in avian species not mammals. Additionally, T4 shown in brackets is available to the PT in both mammals and birds via the portal blood supply, cerebrospinal fluid, or both, whereas melatonin influences PT function in mammals (see text). FSH, follicle-stimulating hormone; GnRH, gonadotropin-releasing hormone; LH, luteinizing hormone; PD, pars distalis; PT, pars tuberalis; T3, 3,5,3′-triiodothyronine; T4, thyroxine; TSH, thyroid-stimulating hormone; 3V, third ventricle (modified from Hazlerigg and Loudon, 2008). Reprinted from Current Biology, volume 18, D. Hazlerigg and A. Loudon, New insights into ancient seasonal life timers, pages R795–R804, copyright 2008, with permission from Elsevier. B. Septal-hypothalamic area of birds. Four loci have been proposed to contain DBP: (1) lateral septal organ (LSO) including the lateral bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BSTL), (2) paraventricular nucleus and medial bed nucleus of the stria terminalis complex (PVN/BSTM); (3) premammillary nucleus (PMM), and (4) paraventricular organ (PVO). The 3 nearly rectangular regions show areas dissected for real-time reverse-transcription PCR: region 1 (R1) Sep/Pre/Ant-Hypo, septal preoptic anterior hypothalamic area; region 2 (R2) Mid-Hypo, middle hypothalamic area; region 3 (R3) Post-Hypo, posterior hypothalamic area. AP, anterior pituitary; CO, optic chiasma; GnRH-1, type 1 gonadotropin-releasing hormone; GnRHR, GnRH receptors; ME, median eminence; NHpC, nucleus of the hippocampal commissure; PP, posterior pituitary; TSM, septopallial mesencephalic tract. Color version available in the online PDF.