Fig. 7.
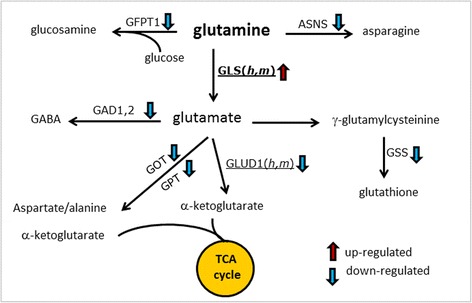
Gene expression analysis of control and ATM-deficient human and mouse brains revealed that ATM deficiency had a huge impact on genes known to take part in brain glutamine metabolism. Presented are a list of genes whose expressions were found to be significantly reduced or increased in ATM-deficient human or mouse brains (>1.5 fold change when compared to control brains, p < 0.05). Upregulated genes are indicated by an black upward arrow next to the gene name; downregulated genes are shown by a downward arrow. Genes whose direction of change was significant in both mouse and human data are shown with underlines
