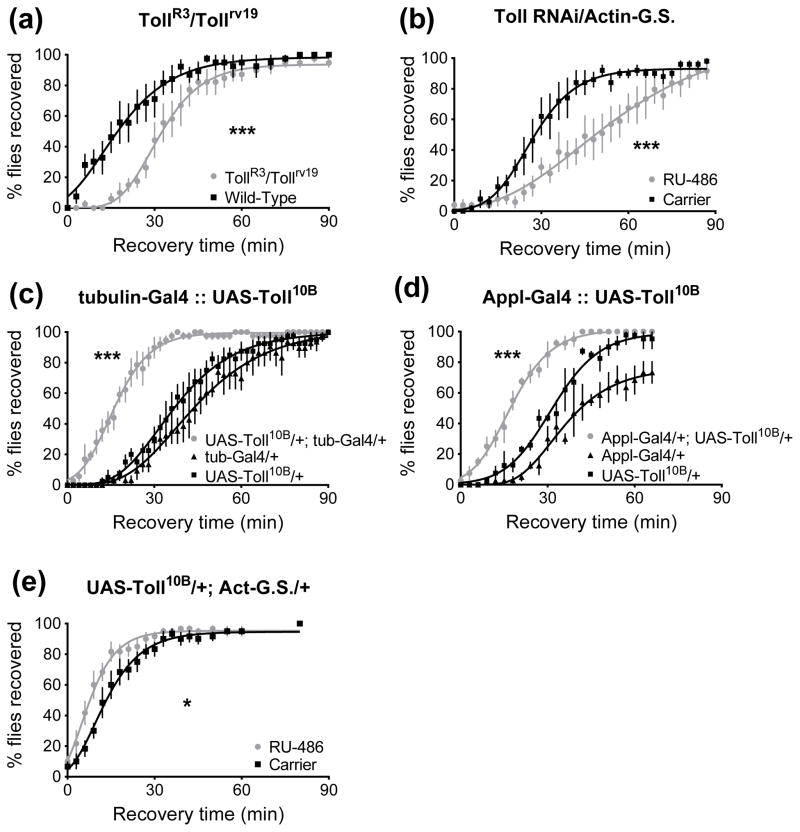
Figure 3.
A Toll loss-of-function mutation or a Toll knockdown decreases resistance, while expression of a constitutively active Toll increases resistance in a recovery from ethanol sedation assay. 0 minutes denotes the beginning of the recovery period. A) Transheterozygous TollR3/Tollrv19 loss-of-function animals recover more slowly than wild-type Canton S (***, p<0.0001). B) RNAi knockdown of Toll via a UAS transgene driven by Actin-GeneSwitch, in which the GeneSwitch inducer was provided for three days prior to testing. Inducer-fed animals (RU-486) recovered more slowly than carrier-fed controls (***, p<0.0001). C) Overexpression of the constitutively active Toll10B allele using the ubiquitous tubulin-Gal4 driver increased resistance (***, p<0.0001 vs. either parental control). D) Overexpression of Toll10B in neurons using the Appl-Gal4 driver increased resistance (***, p<0.0001 vs. either parental control). E) Inducible overexpression of Toll10B only in adults increased resistance (*, p=0.03).