Figure 1.
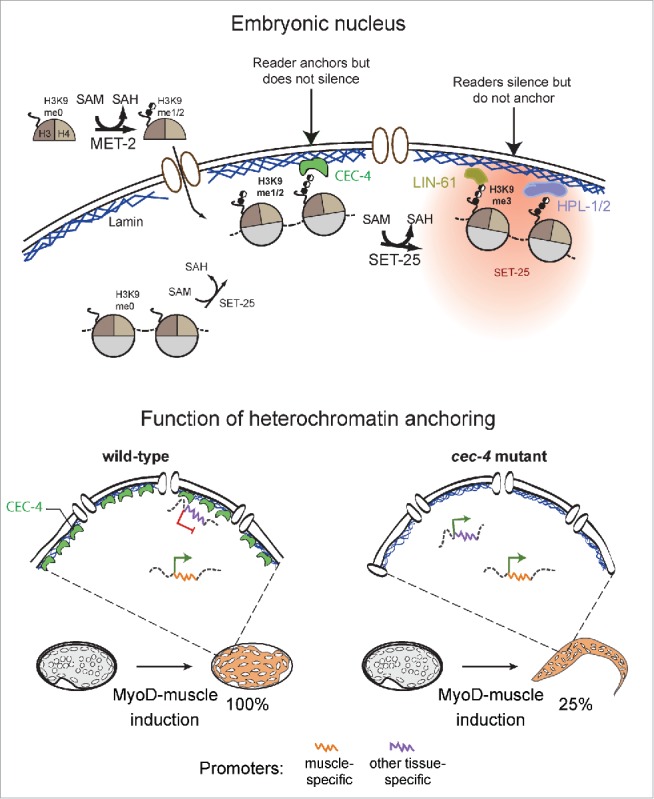
Model of heterochromatin anchoring function. CEC-4 autonomously localizes to the nuclear envelope to read all forms of H3K9 methylated histones. In worms, MET-2 and SET-25 are the enzymes responsible for the deposition of H3K9me1, me2 and me3 (upper half). CEC-4 is a H3K9me reader that anchors but does not silence, while the HP1 homologues, HPL-1 and HPL-2, and the MBT domain protein LIN-61, silence but do not anchor. Cells of wild-type and cec-4 mutant embryos were forced into the muscle differentiation program by inducing the muscle master regulator MyoD (HLH-1 in worms). While 100% of wild-type embryos commit to a muscle fate, 25% of embryos lacking CEC-4 resist full commitment and manage to hatch into larvae-like structures that express markers of other tissues (modified from16). These data represent the first evidence for functionality of a factor solely dedicated to chromatin anchoring in a multicellular organism, and argue that the perinuclear sequestration of heterochromatin promotes the stabilization of a specified cell fate.
