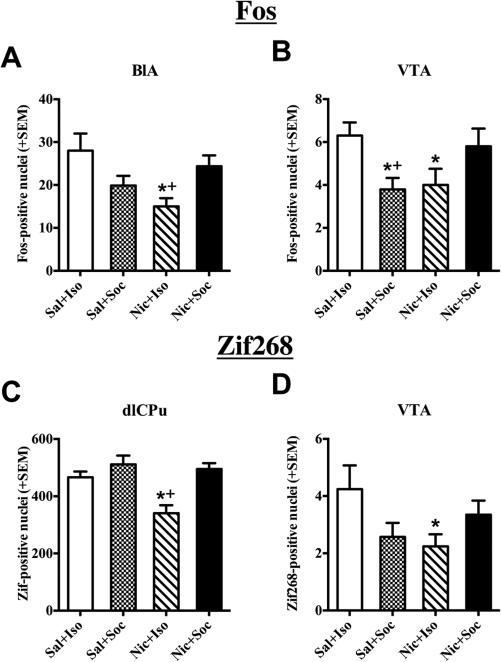
Fig. 5.
Interactive effects of nicotine and social stimuli on IEG expression. Number of Fos- and Zif268-positive nuclei + SEM in regions exhibiting nicotine and social condition interaction effects among rats sacrificed 90-min after the last US conditioning session in the CS+ side of the apparatus. US conditions included either saline (Sal) or nicotine (Nic) injections followed by placement into the initially nonpreferred side of the CPP apparatus either alone (Iso) or with a social partner (Soc) in Experiment 2 (n = 7–10/group). Significant interactions were found in the BLA (A) and VTA (B) for Fos expression and in the dlCPu (C) and VTA (D) for Zif268 expression. Asterisk (*) represents a decrease relative to Sal + Iso negative controls (ps < 0.05, post-hoc independent samples t-test). Plus sign (+) represents a decrease relative to Nic + Soc group (ps ≤ 0.05, post-hoc independent samples t-test).