Table 1. Schematic representation of the morphometric parameters measured and how the results are stated in the paper.
| Parameter | Low | High | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stated in the text | Schema | Stated in the text | Schema | |
| Quantity | ||||
| Density | Low density | 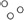 |
High density | 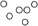 |
| Stained area (SA) | Low SA |  |
High SA |  |
| Relative density/SA of blood vessels corresponding to a given segment compared with the total vascularization | Low proportion of blood vessels | 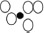 |
High proportion blood vessels |  |
| Size | ||||
| Area | Small |  |
Large |  |
| Length | Short |  |
Long |  |
| Width | Thin |  |
Thick |  |
| Perimeter | Small |  |
Large |  |
| Shape | ||||
| Aspect1 | Round | 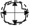 |
Ovoid | 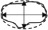 |
| Roundness2* | Few protrusions |
 |
Abundant protrusions |
 |
| Perimeter ratio3* | Irregular outline | 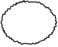 |
Regular outline |  |
| Deformity4* | Weak deformity | 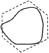 |
Strong deformity | 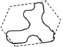 |
| Shape factor5* | Similar to convex contour | 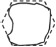 |
Dissimilar to convex contour |  |
| Branching | Unbranched |  |
Branched |  |
Aspect: Major axis/minor axis (of ellipse equivalent to the vessel).
Roundness: Perimeter2/(4*π*area).
Perimeter ratio: Convex contour perimeter/perimeter (convex contour: outline of the polygon best-fitting to the real shape).
Deformity: Convex contour area-area (μm2).
Shape factor: Matches the shape (including the centroids, the area, and information about the orientation) of the vessels and the convex contour (formula: maxi=1,2[│miA-miB│/│miA│]; miA/B=sign (hiA/B)· log(hiA); A/B=Hu moments of real contour/convex contour; í = seven Hu invariant).
All these parameters provide information about the degree of deviation from a round and regular blood vessel, using different approaches.
