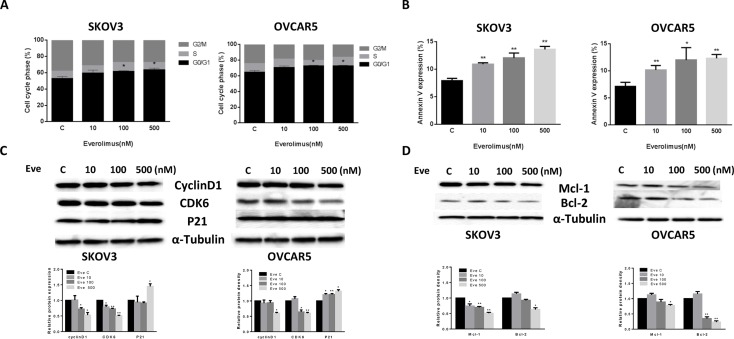
Figure 2. Everolimus induced cell cycle G1 arrest and cellular apoptosis.
The SKOV3 and OVCAR5 cells were cultured for 24 h and then treated with everolimus at varying doses (from 10 to 500 nM) for 48 h. Cell cycle was examined by Cellometer. Everolimus induced cell cycle G1 arrest in a dose-dependent manner in both cell lines (A). The SKOV3 and OVCAR5 cells were treated with varying doses of everolimus for 24 h, and cell apoptosis was examined by an Annexin-V and PI double staining assay via Cellometer. Everolimus significantly increased cell apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner in both cells (B). The cells were treated with various concentrations of everolimus as indicated (from 10 to 500 nM) for 24 h, and the expression of cell cycle proteins were assessed using western blotting analysis. Everolimus decreased the levels of cyclin D1 and CDK6 and increased the expression of p21 in the SKOV3 and OVCAR5 cell lines (C). The protein expression of Mcl-1 and Bcl-2 was decreased after 24 h of treatment with the indicated doses of everolimus in the SKOV3 and OVCAR5 cells (D). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.