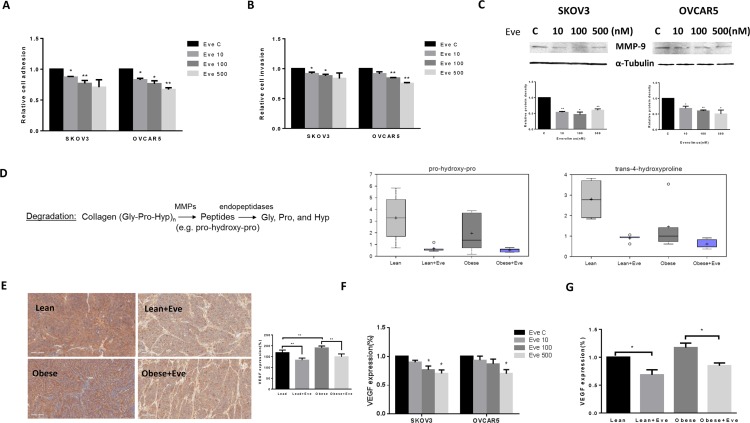
Figure 8. The effect of everolimus on adhesion and invasion in ovarian cancer cells and the obese serous ovarian cancer model.
The SKOV3 and OVCAR5 cells were cultured for 24 h and then treated with everolimus (100 nM) in a laminin coated 96 well plate or BME coated 96 transwell plate for 24 h or 2 h to asses adhesion and invasion in a plate reader, respectively (A and B). Everolimus reduced cell adhesion and invasion in both cell lines. The MMP-9 protein was downregulated in the SKOV3 and OVCAR5 cell lines after treatment with everolimus for 24 h (C). In the KpB mouse model, metabolomic profiling showed that everolimus induced a degradation of collagen metabolites in obese and lean mice (D). Immunohistochemical analysis showed that the expression of VEGF protein was significantly decreased after everolimus treatment in lean and obese mouse (E). The level of VEGF after treatment in lean and obese mouse serum was measured by ELISA assays (F). SKOV3 and OVCAR5 cells were treated with everolimus at 10 to 500 nM for 24 h. The supernates from culture media were measured by ELISA assay. The results showed that everolimus decreased VEGF production in ovarian cancer cell lines (H). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.